Question
Compressibility factor (Z): Real gases deviate from ideal behavior due to the following two faulty assumptions of kinetic theory of gases.
i)Actual volume occupied by the gas molecule is negligible as compared to the total volume of the gases.
ii)Forces of attraction and repulsion among the gas molecules are negligible.
the, extent of deviation of the real gas from ideal behaviour, is explained in terms of compressibility factor (Z), which is function of pressure and temperature for real gas.
For ideal gas, Z = 1
For real gases, Z > 1 or Z < 1
When Z > 1, then it is less compressible because force of repulsion dominates over force of attraction when Z < 1, force of attraction dominates over the force repulsion.
Graph in between Z & P is shown as under
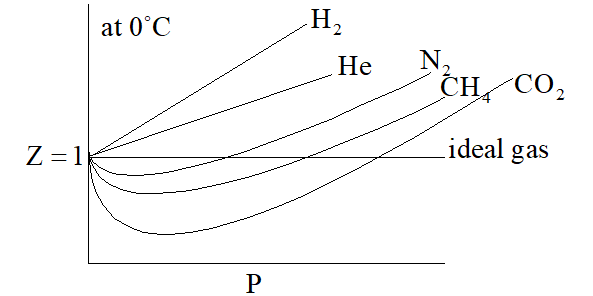
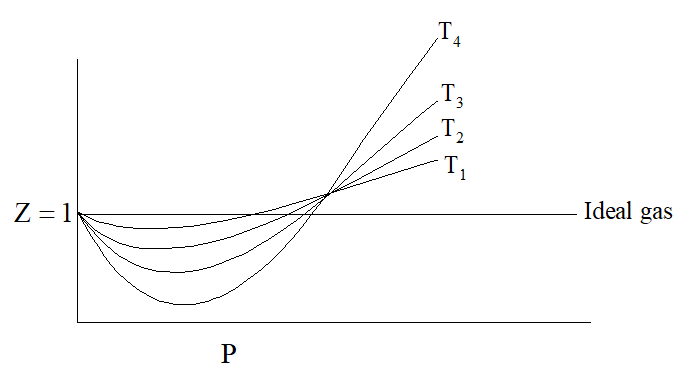
On increasing temperature, Z increases and approaches to unity. Graph between
Z and P at different temperature for the same gas is shown as under:
The van der Waal’s equation of state for 1 mole of gas is as under:
 …(1)
…(1)
Where a and b are van der Waal’s constants.
van der Waal’s constant “a” measures the amount of the force of attraction among the gas molecules. Higher the value of “a”, higher will be the ease of liquefaction.
Case (1)For H2 and He then equation into –I will reduce P(V – b) = RTCase (2) When pressure is too low i.e. for N2 or CH4 or, CO2 then equation (–I) reduces into 
Which of the following statement is correct as shown in the above graph?
- The slope of Z vs P at constant temperature for all real gases, is

- The slope of Z vs P at constant temperature for both He and H2 is
 .
.
- The slope of Z vs P at low pressure for all real gases, at constant temperature is
 .
.
- The slope of Z vs P at high pressure and at constant temperature for real gases is
 .
.
The correct answer is: The slope of Z vs P at constant temperature for both He and H2 is  .
.
Related Questions to study
I, II, III are three isotherm respectively at T1, T2 & T3 temperatures will be in order

I, II, III are three isotherm respectively at T1, T2 & T3 temperatures will be in order

In the figure shown, PT and PAB are the tangent and the secant drawn to a circle. If PT = 12 cm and PB = 8 cm then AB is

In the figure shown, PT and PAB are the tangent and the secant drawn to a circle. If PT = 12 cm and PB = 8 cm then AB is

Find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure

Find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure

‘0’ is the centre of the circle and  then
then 

Therefore the correct option is choice 3
‘0’ is the centre of the circle and  then
then 

Therefore the correct option is choice 3
In the given diagram,  Find the value of DC.
Find the value of DC.

In the given diagram,  Find the value of DC.
Find the value of DC.

In the given figure, find the values of x y, and z

So we have given a quadrilateral where we have to find the angles x, y and z. The measurements of the angles and side lengths of quadrilaterals are used to categorise them. So the values of x, y and z are: 88°, 68°, 92°
In the given figure, find the values of x y, and z

So we have given a quadrilateral where we have to find the angles x, y and z. The measurements of the angles and side lengths of quadrilaterals are used to categorise them. So the values of x, y and z are: 88°, 68°, 92°
ABCD is a quadrilateral. AD and BD are the angle bisectors of angle A and B which meet at ‘O’. If 

So we have given a quadrilateral where we have AO and BO are the angle bisectors of angles A and B which meet at O. The measurements of the angles and side lengths of quadrilaterals are used to categorise them. So the angle AOB is 60 degree.
ABCD is a quadrilateral. AD and BD are the angle bisectors of angle A and B which meet at ‘O’. If 

So we have given a quadrilateral where we have AO and BO are the angle bisectors of angles A and B which meet at O. The measurements of the angles and side lengths of quadrilaterals are used to categorise them. So the angle AOB is 60 degree.
In the unit Square, find the distance from E to  in terms of a and b the length of
in terms of a and b the length of  , respectively
, respectively

Therefore the correct option is choice 1
In the unit Square, find the distance from E to  in terms of a and b the length of
in terms of a and b the length of  , respectively
, respectively

Therefore the correct option is choice 1
ABCD is a Parallelogram,  If DC=16cm, AE = 8 cm and CF = 10 cm, Find AD
If DC=16cm, AE = 8 cm and CF = 10 cm, Find AD

Here we used the concept of parallelogram and identified some concepts of corresponding attitudes. A parallelogram is a two-dimensional flat shape with four angles. The internal angles on either side are equal. So the dimension of AD is 12.8 cm.
ABCD is a Parallelogram,  If DC=16cm, AE = 8 cm and CF = 10 cm, Find AD
If DC=16cm, AE = 8 cm and CF = 10 cm, Find AD

Here we used the concept of parallelogram and identified some concepts of corresponding attitudes. A parallelogram is a two-dimensional flat shape with four angles. The internal angles on either side are equal. So the dimension of AD is 12.8 cm.
Two Rectangles ABCD and DBEF are as shown in the figure. The area of Rectangle DBEF is

So here we used the concept of rectangle and triangle, and we understood the relation between them to solve this question. The total of the triangles' individual areas makes up the rectangle's surface area.So the area of rectangle DBEF is 12 cm2.
Two Rectangles ABCD and DBEF are as shown in the figure. The area of Rectangle DBEF is

So here we used the concept of rectangle and triangle, and we understood the relation between them to solve this question. The total of the triangles' individual areas makes up the rectangle's surface area.So the area of rectangle DBEF is 12 cm2.
In the given figure, ABCD is a Cyclic Quadrilateral  and
and  then
then

In the given figure, ABCD is a Cyclic Quadrilateral  and
and  then
then

In the figure below  If
If  ,
,  and
and  then which of the following is correct ?
then which of the following is correct ?

In the figure below  If
If  ,
,  and
and  then which of the following is correct ?
then which of the following is correct ?

If ABCD is a square, MDC is an Equilateral Triangle. Find the value of x

So here we were given a square PQRS and in that an equilateral triangle STR is present. We used the concept of equilateral triangle to solve the answer. So the angle x is equal to 105 degrees.
If ABCD is a square, MDC is an Equilateral Triangle. Find the value of x

So here we were given a square PQRS and in that an equilateral triangle STR is present. We used the concept of equilateral triangle to solve the answer. So the angle x is equal to 105 degrees.
If PQRS is a Square and STR is an Equilateral Triangle. Find the value of a

So here we were given a square PQRS and in that an equilateral triangle STR is present. We used the concept of equilateral triangle to solve the answer. So the angle a is equal to 75 degrees.
If PQRS is a Square and STR is an Equilateral Triangle. Find the value of a

So here we were given a square PQRS and in that an equilateral triangle STR is present. We used the concept of equilateral triangle to solve the answer. So the angle a is equal to 75 degrees.



