Get the App
For Doctors
Login/Sign-up
About
Health Feed
Find Doctors
The Calf Muscle (Human Anatomy): Diagram, Function, Diseases and More
Last Updated: Apr 08, 2023
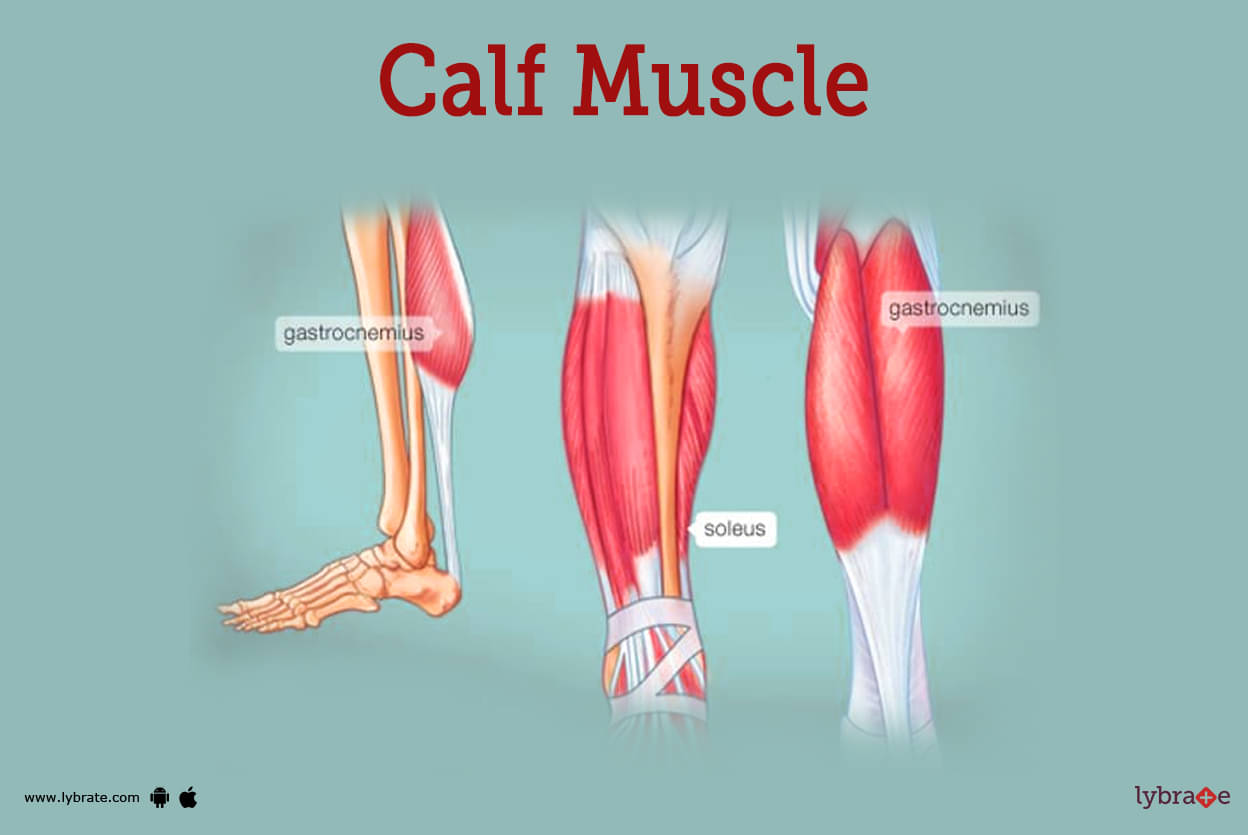
Calf Muscle Image
- The back of the lower leg is home to the calf muscle, also known as the gastrocnemius.The calf muscle can be found in close proximity to the shin bone.
- The calf muscle is composed of two different muscles. that would be the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.The gastrocnemius is the larger of the two calf muscles.
- The gastrocnemius muscle is responsible for the prominence that can be seen beneath the skin.
- It has two heads that, when joined together, make the shape of a diamond.
- It is the larger of the two muscles that make up the calf, while the soleus is the smaller of the two muscles.
- The soleus is a thin muscle that lies underneath the gastrocnemius muscle in the lower leg.
- At the bottom of the calf muscle, the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles come together to form one continuous structure.
- At the very bottom of the calf muscle is where the tough connective tissues that eventually become merged with the Achilles tendon can be found. This tendon attaches to the heel bone at its insertion point.
Functions of Calf muscles
- Calf muscles serve a wide variety of purposes, including assisting in activities such as walking, running, and jumping
- It contributes to the foot's ability to flex more easily
- In addition to that, it helps one stand up straight
Disorders of the Calf Muscles
- Calf Muscle Strain: This occurs when the calf muscle is stretched beyond its normal range of motion, which leads to the tearing of calf muscle fibres, which in turn causes muscle pain. The degree of pain felt in the calf muscles is directly proportional to the amount of muscle that has been torn. The primary varies in intensity from mild to severe.
- Pulled Calf Muscle: Calf muscle strain occurs when the calf muscles are pulled beyond their normal limits, which can lead to a condition known as 'pulled calf muscle.'
- Tearing Of The Calf Muscle: Tearing of the calf muscle is most commonly caused by strains. In the event that you sustain serious injuries, you may suffer a partial or complete tear of your calf muscles.
- Calf Muscle Rupture: It is a condition of the calf muscle in which the calf muscle is completely torn off. Calf muscle rupture is another name for this condition. It makes it impossible to walk and causes excruciating pain in the muscles. In addition to this, the calf muscle will become contracted and will take the shape of a lump or a ball. It was simple to feel its presence through the surface of the skin.
- Calf Muscle Myositis: Myositis of the calf muscle is an extremely uncommon condition of the calf muscle that manifests itself as inflammation of the calf muscles. Infections or autoimmune disorders are the most common causes of this condition.
- Rhabdomyolysis: Rhabdomyolysis is a condition in which the calf muscles break down as a result of prolonged pressure on the calf muscle, as a consequence of the adverse effects of medication, or as a consequence of some other medical condition. This condition most commonly affects the muscles in the calves, but it can also manifest in other muscle groups.
- Cancer Of The Calf Muscle: It is an extremely rare condition that can affect the calf muscle. Sarcoma is the medical term for cancer that can develop in the calf muscles. This condition could also be caused by metastatic cancer, which occurs when cancer that originated in another part of the body spreads to the calf muscle.
- DVT: Deep vein thrombosis is what's meant by the abbreviation 'DVT.'A blood clot forms deep within a vein in the leg, and this condition is known as deep vein thrombosis. It occurs 90% of the time in the proximal region (most commonly in the femoral and iliac areas), and only 10% of the time in the distal region (posterior tibial). It results in discomfort in the calf muscles.
- Baker Cyst: Baker cyst is a lump that develops behind the knee and can be the source of pain or stiffness in the back of the knee.It can dissect into the calf muscles ( present like DVT). It is possible for the calf muscle to rupture, which results in pain, warmth, and redness in the calf.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: DMD is a frameshift mutation that is caused by an X-linked dystrophin mutation. It is characterised by a weakness in the proximal muscles, specifically the calf muscles.
- Calf Pseudohypertrophy: It is an uncommon condition of the calf muscle in which you find enlargement of tissue of muscle due to infiltration of tissues of calf muscles. This condition can be diagnosed by looking for enlargement of muscle tissue in the calf.
- Calf Hypertrophy: The condition known as calf hypertrophy refers to an enlargement of the tissue that occurs in the calf muscles. This may be the result of an infection or other physiological factors.
- Muscle Cramps: Calf muscle cramps are among the most excruciating of all leg cramps. These cramps might be the result of a number of different conditions, such as pregnancy, dehydration, or another condition entirely.
- Tennis Leg: Tennis leg is a condition of the calf muscle in which the gastrocnemius muscle is affected by some injury and other strain. Tennis legs can be caused by a variety of factors.
- Compartment Syndrome: It is a serious condition that is caused by the development of pressure on the calf muscle, which then results in a decrease in supply of oxygen and blood in the calf muscles. This condition is known as compartment syndrome.
- Arterial Claudication: Pain in the calf muscles is a symptom of arterial claudication, which is caused when blood flow is restricted because of a narrowing or blockage in an artery that is responsible for carrying blood.
- Neurogenic Claudication: Neurogenic claudication is a condition in which the nerves that pass through the legs or originate in the calf muscles become compressed. This impairs the ability of the lower legs to communicate with one another.Pain while walking, pain after standing for an extended period of time, and pain that can also be felt in the thighs, lower back, or buttocks are all examples of neurogenic claudication symptoms.When a person is experiencing this kind of pain, bending forward at the waist may help relieve some of the discomfort.
- Achilles Tendinitis: Injury or inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which is the tendon that runs from the heel bone to the calf muscle. Achilles tendinitis is the name given to the pain that occurs as a result of this system.
- Exertional Compartment Syndrome: Exertional compartment syndrome is a condition of the calf muscle in which the calf muscle experiences pain during exercise as a result of fluid filling up that muscle. This pain is caused by the fluid filling up the compartment in the calf muscle. The most prominent symptoms include numbness, obvious bulging or enlargement of the muscles, or difficulty moving the affected foot.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Diabetes mellitus can cause nerve damage in the calf muscles and other nerves in the legs, a condition known as diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes mellitus can cause nerve damage in the calf muscles and other nerves in the legs. The most prominent symptoms are a tingling and numbing sensation, as well as possible mild pain and discomfort that radiates to the calf muscles.
- Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar fasciitis is a condition characterised by inflammation of the tissue that makes up the plantar fascia, which is situated at the base of the foot. It is because of an excessive shortening of the calf muscle. The calf muscles do not provide support for the flexion of the foot in this position.
- Varicose Veins: Varicose veins are a condition that causes veins to protrude outward from the legs in the form of a cord. This condition is known as varicose veins. The majority of cases of this condition are brought on by damage to the valves of the heart. This condition almost always affects the legs, particularly the region surrounding the calf muscle, and as a result, it can cause pain, cramping, throbbing, and aching.
- Calf Muscle Dysfunction: Patients who suffer from cardiovascular disease are more likely to have this condition. In addition, hypothyroidism is associated with dysfunction in the calf muscles. Diseases of the liver, kidneys, and blood vessels, as well as diabetes and peripheral artery disease (PAD), are some examples of conditions that can impair the function of the calf muscles' pump.
Test Of The Calf Muscle
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging: It is most frequently referred to as M.R.I. The purpose of this examination is to obtain an in-depth structure of the calf muscles as well as any other soft tissues in the body. This method identifies the intricate structures of soft tissues by making use of a high-power magnet in conjunction with a computer.
- Computed Tomography: This diagnostic procedure is more commonly referred to as a CT scan. This examination made use of X-ray waves and a computer in order to gain a detailed understanding of the structure of the calf muscles or any other muscles associated with or located nearby the calf muscles.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the calf muscle is a diagnostic procedure that makes use of a machine that generates sound waves of a high frequency. The calf muscle, as well as the ligaments and tendons surrounding it, are penetrated by these sound waves, which allows for the detailed structure of the calf muscle to be displayed on the computers of medical professionals.
- Phlebography: The study of phlebography Venography is another name for this procedure. A venogram will be taken immediately following the injection of a specific dye into the veins or bone marrow of the patient.
Calf Muscles Treatments
- Home Remedies: Home remedies for calf muscle strains include applying ice to the affected area, wrapping the injured area in elastic bandages called compression, and so on. These are just a few examples. A significant component of its recovery consists of periods of rest and protection.
- Elevation: Elevation is when you put your leg on a pillow so that it is in an elevated position. This allows circulation to occur in the calf muscles, which helps reduce swelling.
- Surgery: Surgery of the calf muscle may be necessary in order to remove carcinoma of the calf muscle (also known as sarcoma) or to repair a calf muscle that has been completely torn.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that includes Patients might be prescribed cancer-fighting drugs as part of their treatment for sarcoma or other cancers that affect the calf muscle. This helps ensure that the disease is eradicated as effectively as possible.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is a form of treatment that involves directing high-energy radiation at cancer cells in the calf muscle. This type of therapy is helpful in the treatment of sarcoma and other types of carcinoma that can occur in calf muscles.
- Physiotherapy: There are many cases of injuries or weaknesses in calf muscles that could be treated by exercises and other programs which are designed by a professional physiotherapist to restore the strength of calf muscles, which helps in its proper function. There are many cases of injuries or weaknesses in calf muscles that could be treated by exercises and other programmes.
Calf Muscle Medicines
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are a type of medication that are used to treat bacterial conditions that affect the calf muscles, such as myosotis. Amoxicillin is a member of this class of medication.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone and other drugs similar to cortisone may be prescribed to patients suffering from certain types of myositis that manifest in the calf muscle. These medications function by dampening the activity of the immune system.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers: OTC, or over-the-counter, pain relievers include the following: Medicines belonging to this category are taken to treat musculoskeletal pain and inflammation, respectively. Ibuprofen is a typical medication used by students in this group.
- Antiviral medicine: Amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, oseltamivir, ribavirin, acyclovir, ganciclovir, and foscarnet are just some of the medications that belong to this class that is frequently prescribed. In the field of calf medicine, medicines belonging to this category are the ones that are utilised for the treatment of viral infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 3 calf muscles?
The "calf muscle," as it is most usually referred as, is made up of the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles.
Why do calf muscle pain?
Cramping, which occurs when muscles suddenly contract, is typically the source of calf pain. If you have been performing new workouts, if you are dehydrated, or if you are mineral deficient, this could occur.
How to reduce calf muscle?
Walking frequently is a low-impact method of losing calf fat.
How to build calf muscle?
Standing calf raises are among the greatest exercises for gaining calf size.
How to strengthen calf muscles?
Excellent calf-strengthening workouts include walking, hiking, and running.
How to stretch calf muscles?
Keep one leg straight back with the heel flat on the floor while holding onto a chair. To feel a stretch in your leg, slowly bend your elbows, front knee, and hips forward. Keep this stance for 30 to 60 seconds. Change the position of one leg, then repeat with the other.
Why are calves called second heart?
Due to its similar function to the heart's within the circulatory system, the calf muscle is frequently referred to as the second heart.
How do you treat a strained calf muscle?
A person with a pulled or strained calf muscle should generally take it easy to avoid doing further harm to the muscle. For those with a slight sprain, the following treatments may help alleviate symptoms: Wraps and bandages, ice and heat therapy Elevating the hurt leg and using over-the-counter (OTC) medicines.
Delhi
Mumbai
Chennai
Bangalore
Index
Table of content
Content Details
Written ByDrx Hina FirdousPhD (Pharmacology) Pursuing, M.Pharma (Pharmacology), B.Pharma - Certificate in Nutrition and Child CarePharmacology
Reviewed By
Find Orthopedic Doctor near me
Ask a free question
Get FREE multiple opinions from Doctors
posted anonymously