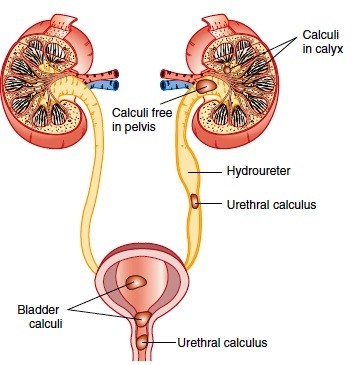
Renal Calculi / Kidney Stones
Kidney stone / Renal calculi is a solid crystalline mass made of various minerals due to improper diet or faulty metabolism. Renal calculus is generally formed in kidney but can also form in various parts of urinary system, for which they are named accordingly, like Renal, Uretric, Cystic (Urinary bladder) Or Urethral calculi.
Types of Renal stones:
Commonly found types of kidney stones are formed of Calcium Oxalate, Uric Acid, Struvite, Cystine, etc.
Calcium Oxalate: Calcium stones are the most common and are made of calcium oxalate. Frequent consumption of high oxalate foods like spinach, chocolates, peanuts and fried potato increases the risk of developing calcium stones. However, even calcium stones are most common type, one should not avoid diet rich in calcium as your bone density depends on it.
Uric acid: Another common renal stone, mostly found in men than in women. People with gout or family history of gout are more prone to get uric stones. Diet rich in purine disturbs the metabolism and turns the urine more acidic, triggering the stone formation. Purine is found abundant in animal proteins, such as fish, shellfish, and red meats.
Struvite: Less common and found mostly in women with urinary tract infections. These stones vary in size from large to small and can cause urinary obstruction. These are triggered by high purine content.
Cystine: These stones are rare in occurrence and can be found in both men and women. Diet which increases the acidity of urine may trigger cystine stone formation. Genetic disorder of cystinuria may trigger the stone formation.
Risk trigger factors:
Risk prone individuals can be both men and women between 20 to 50 yrs, with or without family history. Few other risks triggers are dehydration, obesity, diet rich in animal protein, excessive salt, glucose and few medical conditions which disturbs the calcium absorption like hyper-parathyroid condition, gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel syndrome. The risk of stone formation triples when Less than a liter of urine is formed. Scanty urine condenses and triggers the accumulation of minerals on excretory waste including epithelial cells.
General Indication:
kidney stones are generally symptom less until the stone begins to move. Kidney stones are known to cause severe excruciating pain, known as renal colic. The character and region of pain depends on side, location and size of the stone. In men, pain may radiate from mid back to the groin area. The pain is intermittent (comes & goes) in nature. There may be associating symptoms like hematuria (blood in the urine) which may reflect as red, pink or brown urine, vomiting, nausea, chills and fever with or without infections.
Complication to morbidity:
Usually renal calculus doesn't have complications except when the stone is big enough to block the passage. Passage of stones down the ureter can cause spasms, irritation and scratches on ureter wall. This causes blood to appear in the urine which may lead to kidney infections. Sometimes stones block the flow of urine, called urinary obstruction causing hydronephrosis. Urinary obstructions can lead to kidney infection and kidney damage.
Detecting a Renal Stone:
Diagnosis of kidney stones requires a complete medical assessment and a physical examination to determine the type, location and obstruction. Blood tests are done for minerals like calcium, phosphorus, uric acid and electrolytes to determine the type of stone, whereas blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine to assess kidney function. Urinalysis to check for crystals, bacteria, blood, and white cells examination of passed stones to determine their type.
Radiological tests like Abdominal X-rays (KUB), Intravenous pyelogram (IVP), Retrograde pyelogram, MRI scan of the abdomen and kidneys, abdominal CT scan are done to determine the location of the stone and to rule out obstruction.
Getting Cure:
Treatment is planned according to the type and location of stone. Medication is generally according to the type of stone. Pain killers are prescribed when there is severe pain during stone movement. Few procedures are also performed to eradicate the renal stone like Lithotripsy, Tunnel surgery (percutaneous nephrolithotomy), Ureteroscopy, etc.
Homeopathic Remedies:
There are various miraculous Homeopathic remedies which prevents and eradicates the renal stone. The top ranking homeopathic remedies are Berberis Vul, Ocimum Can, Hydrangea, Solidago, Lycopodium, Pareira, Urtica Urens, Terebinth, Bell, etc. All these medicines are specific to side, type, location and character, etc of the stone.
Prevention:
Proper hydration is a keynote measure. Drink plenty of water, at-least 12-15 glasses every day to increase the amount of urine to flush the kidneys. Water can be supplemented by clear fluids like, fruit juices, soda, lemonade, etc. Eating food less in oxalate, animal protein and salt, helps to reduce the risk of stone formation.
Dr Harkirat S Wilkhoo www.wellnessdrwilkhoo.com