Methods of International Trade Payment
In international trade, one may come across a number of modes of payment which are being used for receiving trade proceeds. These are:
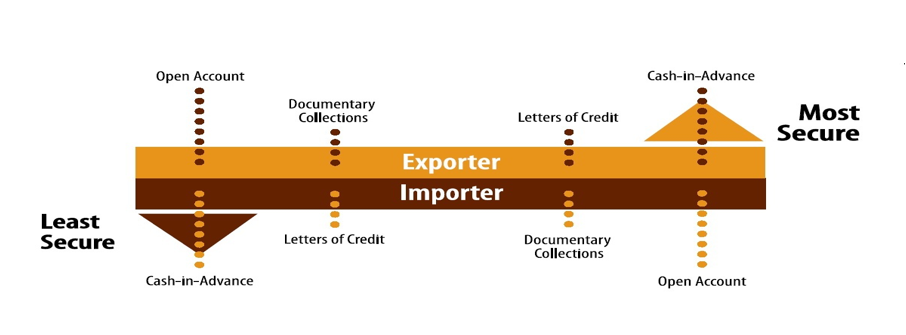
- Cash in Advance
- Open Account
- Documentary Collection
- Documentary Credit
- Cash in Advance: In this method of payment, the buyer places the funds at the disposal of seller (exporter) prior to shipment of goods in accordance with the sales/purchase contract, which is certainly to be concluded between exporter and importer before the trade transactions. If the exporter is not sure about the buyer's credit or there are other circumstances which cast doubt on the certainty of getting paid, a last resort is to ask for cash in advance. This may be acceptable to a first-time buyer who trusts seller to deliver the goods. In the long run, however, it may not be competitive and buyers will not want to continue importing goods if they can turn to other suppliers offering better terms.
- Open Account System: At the other end of the range of payment methods is the open account system. This is an arrangement between the buyer and seller (Sales/Purchase contract) whereby the goods are manufactured and delivered before payment is required. Open account provides for payment at some stated specific future date and without requiring the buyer to issue any negotiable instrument evidencing his legal commitment. The seller must have absolute trust that he will be paid at the agreed date. Though the seller can avoid a lot of banking charges and other costs, but he has no security that he will be receiving payment in due course.
- Documentary Collection: This is an arrangement (Sales/Purchase contract) whereby the goods are shipped and the relevant bill of exchange/Draft is drawn by the seller on the buyer and documents are sent to the seller's bank with clear instructions for collection through one of its correspondent banks located in the buyer's domicile. In this method, the exporter will hand over the shipping documents to his bank and ask it to forward the documents to the buyer's bank, with instructions to release them to the buyer on payment of his invoice. This is called cash against documents (CAD). The exporter can also give the buyer trade credit by drawing a bill of exchange on him and requiring him to accept the bill when he collects the documents. This is called documentary collection against acceptance, or documents against acceptance (DAA) because the buyer accepts the bill of exchange.
- Documentary Credits: The documentary credit or letter of credit is an undertaking issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer (or for its own account), to pay the beneficiary (exporter) the value of the draft and/or documents provided that the terms and conditions of the credit are complied with. This is the most frequently used method of payment in international trade. Although one of the costliest, it is open considered the most secure because the buyer is assured that the seller will be paid only when the documents representing goods have been delivered. Conversely, the seller is assured that the buyer will receive the documents for ultimate delivery of the goods only when payment has been made. The security of the transaction is assured by one or more third parties. This is normally the buyer's bank (issuing bank), which issues the letter of credit (L/C) and the seller's bank (advising/confirming bank), which informs the seller that the L/C has been issued and perhaps adds its confirmation to the L/C (in other words, guarantees the payment if the seller wants to be sure the issuing bank will not default)
- In addition to commitment of making payment by a bank to the exporter, the documentary credit provides legal security to the involved parties as it may operate within framework of ICC's (International Chamber of Commerce) Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP-600). UCP-600 is an international codification of actual business practices, based on the experience of bankers, exporters and importers.
- The Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP) is a set of rules on the issuance and use of letters of credit. The UCP is utilized by bankers and commercial parties in more than 175 countries in trade finance. Some 11-15% of international trade utilizes letters of credit, totaling over a trillion dollars (US) each year.
