#International Trade - Letter of Credit
Dear Professional Friends,
The International Trade has multiple risks as highlighted in my previous article on "Credit Risk" which required to be mitigated while transacting with international counterparts through Letter of Credit.
I will touch upon the important aspects of LC in my latest insight.
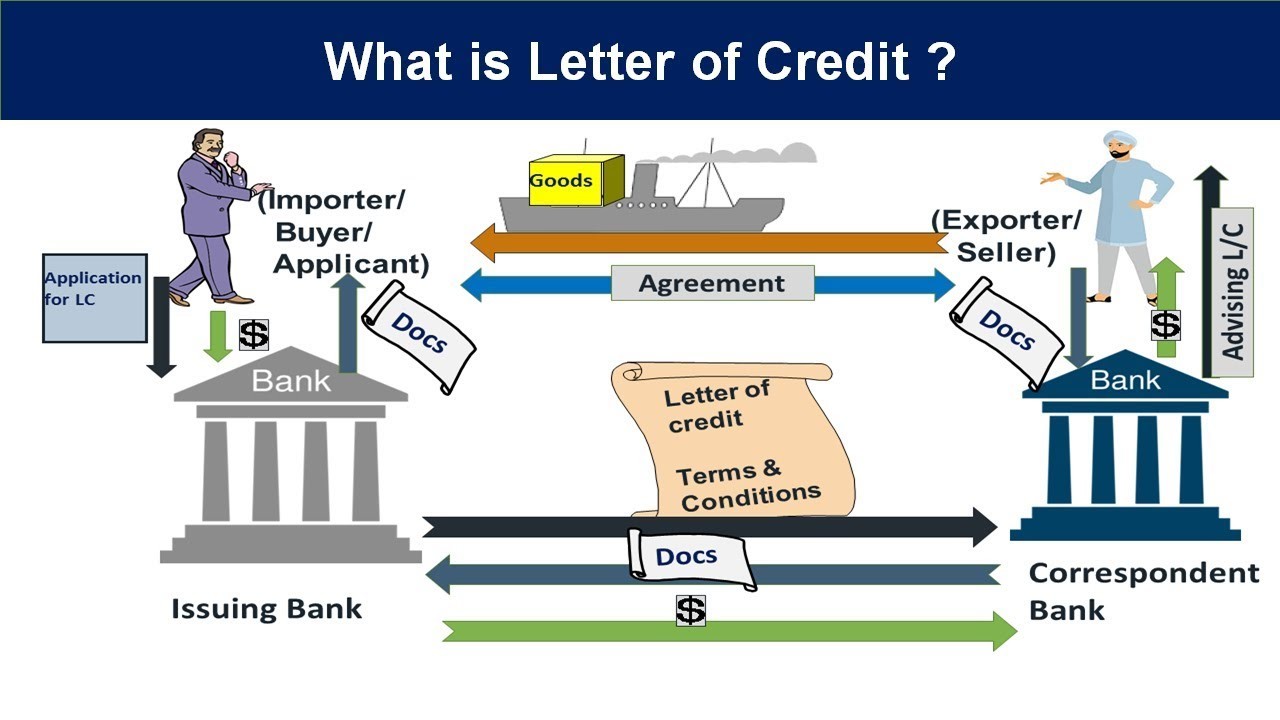
The first thing comes to our mind is - What is Letter of Credit?
A letter of Credit is a "Bank Guarantee" to the seller for the buyer's timely payment or to cover the full or remaining amount of the purchase in the event of default by the buyer.

Before moving further, we need to understand the important terms used under LC transactions:
Applicant- Buyer or the party on whose request the credit is issued.
Beneficiary- Seller or the party in whose favor a credit is issued.
Advising Bank- The bank that advises the credit at the request of the issuing bank.
Issuing Bank -The bank that issues a credit at the request of an applicant.
Confirming Bank - The bank that adds its confirmation to a credit upon the issuing bank's authorization or request.
Nominated Bank-The bank with which the credit is available or any bank in the case of a credit available with any bank.
Complying presentation- Means a presentation that is in accordance with the terms and conditions of the credit, the applicable provisions of these rules, UCP 600 and international standard banking practice.
Negotiation- Means the purchase by the nominated bank of drafts (drawn on a bank other than the nominated bank) and/or documents under a complying presentation, by advancing or agreeing to advance funds to the beneficiary on or before the banking day on which reimbursement is due to the nominated bank.
Now we will also go through the benefits of LC before moving ahead on LC.
# Benefits of LC in International Trade:
1) Can create security and build mutual trust for buyers and sellers in trade transactions. Avoids potential disputes overseas and saves Arbitration/ Legal cost.
2) Makes it easier to structure the documentation and transaction between involved parties. Letters of credit can be personalized with terms that are tailored to the circumstances of each transaction with specific Business needs.
3) LC acts as guarantee to a seller / supplier that they will get paid and ensures to buyer that supplier will get paid only after submission of authenticated documents at banks counter to avoid the title disputes later on.
4) Helps both supplier and buyer to participate in international trade and expand business without much due diligence on personal level as banks bear the risk in case of default.
# There are several types of letters of credits in international trade:
1) Revocable versus Irrevocable - An irrevocable letter of credit cannot be changed without the written consent of all parties including the beneficiary while a revocable letter of credit can be change or withdrawn without notifying the beneficiary.
2) Confirmed versus Advised - Confirmed LC is preferred, as the Confirming Bank promises to pay while Advised LC does not guarantee the creditworthiness of the Opening Bank.
3) Straight versus Negotiation- A negotiation letter of credit can be presented to any bank while a straight letter of credit can only be paid in the country of the Paying Bank
4) Sight versus Usance- At sight means the Beneficiary is paid as soon as the Paying Bank has determined that all necessary documents are in order while Usance time can be between 30 and 180 days after the bill of lading date.
Mostly international suppliers prefer irrevocable confirmed usance LC.
Further, the LC must state whether it is available by sight payment, deferred payment, acceptance or negotiation. (UCP 600 - Article 6- b)
1) Sight Payment: The payment is made as soon as the complying presentation is seen by the issuing bank, or the bank nominated in the letter of credit.
2) Deferred Payment: The payment which is made after a period of time that is specified in the letter of credit. The payment period is usually determined as specific number of days after the date of presentation or the date of the transport document. Bill of exchange or draft is not required under deferred payment.
3) Acceptance: Acceptance refers to acceptance of a bill of exchange which is drawn on the bank mentioned in the letter of credit to be presented with the other required documents and payment at the maturity.
Besides the availability of LC, it is important to comprehend the documents required to be presented under the LC terms (Documentary LC) under clause 46A:
1) Financial Documents -
Bill of exchange: BoE is a negotiable instrument guaranteeing the payment of a specific amount of money, either on demand, or at a set time
2) Commercial Documents:
Commercial Invoice: An invoice or bill is a commercial document issued by a seller to the buyer, indicating the products, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller has provided the buyer.
3) Shipping Documents:
Bill of Lading -(A document issued by a carrier to a shipper, acknowledging that non specified goods have been received on board as cargo for conveyance to a named place for delivery to the consignee who is usually identified), Insurance Certificate, Certificate of Quantity, Certificate of Quality, Commercial, Official or Legal Documents.
4) Official Documents: Origin Certificate, Inspection Certificate

# Specimen of Documents required under clause 46A-
- Signed Commercial Invoice (Original with Copies)
- Bills of Lading (3/3 with Copies)
- Certificate of Quantity (Original with Copies)
- Certificate of Quality (Original with Copies)
- Certificate of Origin (Original with Copies)
- Original Letter of Credit
- Original LC amendments Copy
or
- Commercial Invoice (Original with Copies)
- Letter of Indemnity (LOI)
The transmission of LC from bank to bank happens through Swift routes.
What is Swift- Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication
Swift provides a network to allow financial and non-financial institutions to transfer financial transactions through a 'financial message‘ which includes the literal "MT" (Message Type). This is followed by a 3-digit number that denotes the message type, category, and group.
Overview of SWIFT MT Categories:

The Format of Documentary LC:


Chief Manager at GAIL (I) Ltd.
11moSir please enlighten how block chain technology has impacted the traditional process of letter of credit