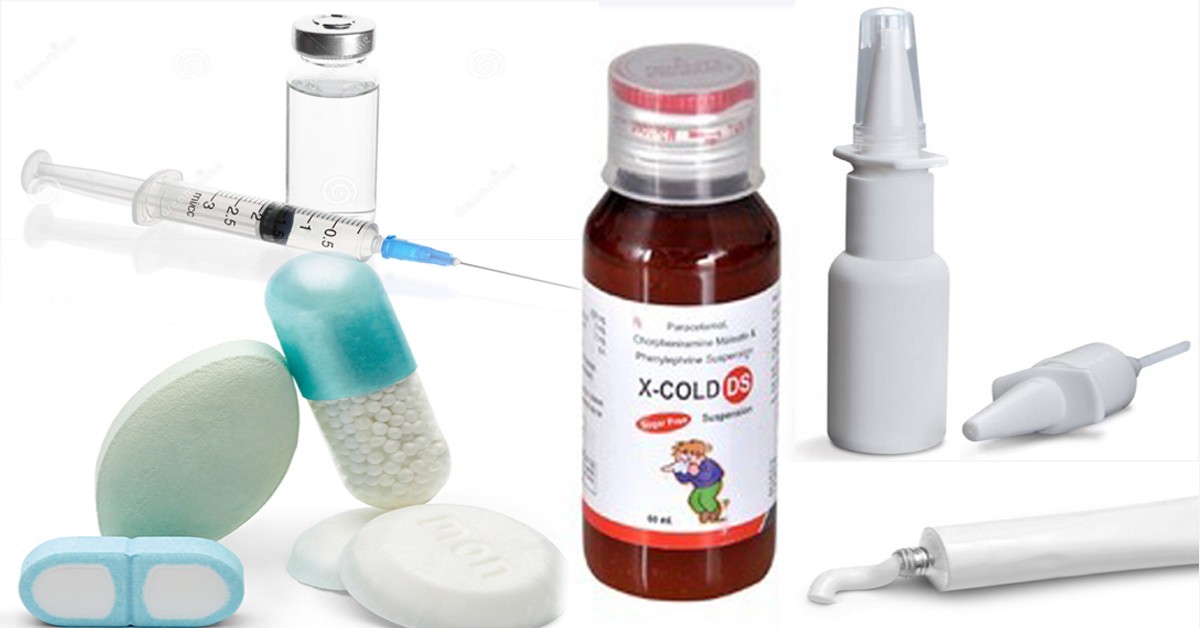
Different types of pharmaceutical dosage forms
Pharmaceuticals are an invaluable tool for the medical field, providing a wide range of treatments and cures for various illnesses. But, with so many different dosage forms available for each type of drug, it can be difficult to know which is best for your specific needs. In this article, we'll provide an overview of the different types of pharmaceutical dosage forms, their advantages and disadvantages, and explain why you should consider each one when making your decision.
Introduction
It is estimated that there are over 10,000 different types of pharmaceutical dosage forms. The most common dosage forms include tablets, capsules, liquids, powders, and gels. Each form has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Tablets are the most common type of pharmaceutical dosage form. They are easy to take and can be taken with or without food. Tablets can be crushed or dissolved in water for patients who have difficulty swallowing them whole. Capsules are another common type of dosage form. They are typically made of two halves that fit together and contain a powder or liquid medication. Capsules can be taken with or without food and are usually swallowed whole.
Liquids are often used for children or adults who have trouble swallowing pills. They can be taken with or without food and come in various flavors to make them more palatable. Powders can be mixed with water or other liquids to create a drinkable solution. They are typically used for patients who cannot swallow pills or capsules. Gels are thick, sticky solutions that come in tubes or packets. They can be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes and are typically used for local treatments such as mouth sores or vaginal infections.
Different pharmaceutical dosage forms are created to help patients take their medication in the most effective way possible. Depending on the patient’s needs, their doctor will prescribe a specific dosage form of medication. Some of the most common pharmaceutical dosage forms include:
Oral Dosage Forms: Capsules, tablets, powders, and liquids are all oral dosage forms of medications. These are taken by mouth and typically work quickly since they’re easily absorbed into the bloodstream through the gastrointestinal tract.
Injectable Dosage Forms: Injectable medications are given directly into the muscle or fat tissue, veins, or joints. They’re generally used when oral medications aren’t an option or when a faster delivery method is necessary.
Topical Dosage Forms: Topical medications are applied directly to the skin and work by being absorbed into the body through the skin. They’re used to treat conditions like acne, athlete’s foot, and dandruff.
Suppositories: Suppositories are small, solid doses of medication that are inserted into the rectum or vagina where they dissolve and are then absorbed into the body. They’re often used when patients can’t take oral medications or when a faster delivery method is necessary.
Types of Dosage Forms
In general, dosage forms can be classified into three broad categories: solid, liquid, and semisolid. Each of these categories can be further divided into subcategories.
Solid dosage forms are the most common type of dosage form. They include tablets, capsules, powders, and granules. Tablets are the solid dosage form that is most familiar to people. They are typically made by compressing a powder into a disk shape. Capsules are similar to tablets, but they are usually smaller and have a shell that dissolves in the stomach. Powders are dry products that must be mixed with water or another liquid before they can be taken. Granules are larger than powders and can be taken without being mixed with water first.
Liquid dosage forms include solutions, suspensions, elixirs, and syrups. Solutions are clear and contain dissolved drugs. Suspensions are cloudy because the drug is not completely dissolved. Elixirs are sweetened solutions that may also contain alcohol. Syrups are thick liquids that contain dissolved drugs and syrup base (such as sugar).
Semisolid dosage forms include creams, gels, ointments, pastes, lotions, and suppositories. Creams and ointments both contain oil and water; however, ointments contain more oil than cream do while creams contains more water than ointment do. Gels only contains liquid; however it has a different chemical
- Solid Dosage Forms
Solid dosage forms are the most common type of pharmaceutical dosage form. They are easy to administer and can be taken orally, by inhalation, or rectally. Solid dosage forms include tablets, capsules, powders, and granules. Tablets and capsules are the most common solid dosage form. They can be manufactured in a variety of shapes and sizes. Powders and granules are less common, but they offer certain advantages over tablets and capsules.
- Liquid Dosage Forms
There are four different types of liquid dosage forms: suspensions, syrups, elixirs, and solutions.
Suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures in which the active ingredient is finely divided and suspended in a liquid vehicle. The suspension must be shaken before each use to ensure that the correct dose is delivered with each administration. Syrups are sweetened, concentrated solutions that contain solids dissolved in a liquid vehicle. They are often used as vehicles for cough suppressants and expectorants. Elixirs are clear, sweetened solutions that contain both insoluble and soluble solids dissolved in a liquid vehicle. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures in which the active ingredient is completely dissolved in a liquid vehicle.
Each type of liquid dosage form has its own advantages and disadvantages. Suspensions may not be palatable or visually appealing, but they offer the advantage of being relatively easy to prepare at home. Syrups can be quite sweet, making them unpalatable for some patients, but they offer the advantage of being easy to take on the go. Elixirs can be expensive to prepare, but they offer the advantage of being shelf-stable for long periods of time. Solutions offer the advantage of being easy to administer, but they may not be as effective as other dosage forms because of their rapid absorption rate.
- Inhalation Dosage Form
Inhalation is one of the most common routes of administration for drugs. It offers many advantages over other routes, such as oral administration, including rapid onset of action, high bioavailability, and avoidance of first-pass metabolism. Inhalation also allows for targeted delivery to the lungs, which is the desired site of action for many drugs used to treat respiratory conditions.
There are a variety of inhalation dosage forms available, including powders, aerosols (pressurized metered-dose inhalers), nebulizers (liquid aerosolators), and dry powder inhalers. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages that should be considered when choosing a formulation for a particular patient.
Powders are the simplest form of inhalation drug and can be administered using a variety of devices, such as handheld inhalers or nebules. They are often used for short-acting drugs that require quick onset of action, such as bronchodilators. However, powders can be difficult to dose accurately and may cause irritation to the lungs if not inhaled properly.
Consols are pressurized metered-dose inhalers that deliver a precise amount of medication with each puff. They are convenient and easy to use, making them a good choice for patients who require long-term therapy. Consols are also less likely to cause lung irritation than powders. However, they do require coordination between actuation and inhalation, which can be difficult for some patients.
- Semi-Solid Dosage Form
A semi-solid dosage form is a type of pharmaceutical dosage form that is a semisolid material. This type of dosage form can be in the form of a cream, gel, lotion, ointment, paste, or suppository. Semi-solid dosage forms are used to treat conditions such as acne, athlete's foot, cold sores, diaper rash, earache, insect bites and stings, poison ivy/oak/sumac, and vaginal yeast infections.
- Parenteral Dosage Form
Parenteral dosage forms are those that are administered via a route other than the gastrointestinal tract, such as intramuscular, intravenous, or subcutaneous injection. Because parenteral administration bypasses the body’s natural defenses, such as the skin and mucous membranes, it is important that parenteral products be sterile and free of microorganisms.
Parenteral dosage forms are typically either solutions or suspensions. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more substances in which the particles of one substance are dissolved in the other. Suspensions are heterogeneous mixtures in which the particles of one substance are dispersed throughout another.
Some common types of parenteral dosage forms include:
- Intramuscular Injections: In intramuscular injections, medication is injected into the muscles using a needle and syringe. Commonly injected medications include vaccines, antibiotics, and hormones.
- Intravenous Injections: In intravenous injections, medication is injected directly into the veins using a needle and syringe. This route of administration allows for rapid absorption of the medication into the bloodstream. commonly injected medications include fluids, electrolytes, and medications used during surgery.
- Subcutaneous Injections: In subcutaneous injections, medication is injected just below the skin using a needle and syringe. This route of administration is often used for self-administration of insulin by people
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
When it comes to taking medication, there are different ways that the active ingredient can be delivered to your body. The three main types of pharmaceutical dosage forms are tablets, capsules, and liquids. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages that you should take into consideration before making a decision about which form is right for you.
Tablets: Tablets are the most common type of pharmaceutical dosage form. They are easy to take and can be taken with or without food. They also tend to be less expensive than other dosage forms. However, tablets can be difficult to swallow and may not be suitable for people who have trouble swallowing pills.
Capsules: Capsules are another popular type of pharmaceutical dosage form. They are easy to take and can be taken with or without food. Capsules are also less likely to cause stomach upset than tablets. However, they can be more expensive than tablets and may not be suitable for people who have trouble swallowing pills.
Liquids: Liquids are the least common type of pharmaceutical dosage form. They are easy to take and can be taken with or without food. Liquids are also less likely to cause stomach upset than tablets or capsules. However, they can be more expensive than other dosage forms and may not be suitable for people who have trouble swallowing pills.
Subscribe Pharmaguideline on Youtube
graphic designer
2moIs there a dosage form of liquids called mixture? When it contain Alcohol and liquids in the same proportion
10 years experience in QC microbiology department
1yMDS (Mouth dissolving strip)
Analyste contrôle qualité chez WORLD MEDICINE ALGERIA
1yThank you Sir.