Table of Contents
- Understanding Patent Infringement
- What is Patent Infringement?
- How to Identify Patent Infringement
- Case Study: Company A (Widget Co.) vs. Company B (Gadget Co.)
- Benefits of Patent Research and Analysis
- Defenses Against Patent Infringement
- Possible Consequences of Patent Infringement
- Using ktMINE for Patent Infringement Analysis
- Importance of Comprehensive Patent Infringement Research for Lawyers and Law Firms
Patent infringement is a critical issue faced by innovators and companies worldwide. As intellectual property plays an increasingly vital role in various industries, it becomes essential to understand the complexities and consequences associated with patent infringement. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to patent infringement, with a focus on the role of ktMINE and its innovative product in assisting both lawyers and law firms in patent infringement research and analysis.
Understanding Patent Infringement
Patent infringement is of paramount importance in the realm of intellectual property law. It refers to the unauthorized use, manufacture, sale, or distribution of a patented invention, violating the exclusive rights granted to the patent holder. Understanding patent infringement is crucial for both patent holders seeking to protect their inventions and accused parties looking to defend against infringement claims.
ktMINE is a leading provider of intellectual property data and analytics. Our innovative platform empowers legal professionals with comprehensive and accurate information for patent research and analysis. Specifically, ktMINE offers a depth of data that is not available in other platforms providing royalty rates, agreement terms, settlement information, litigation, and additional transactional intelligence to support patent infringement cases. With an extensive collection of global patent data, ktMINE offers valuable insights to lawyers and law firms, assisting them in identifying and analyzing patent infringement cases effectively.
What is Patent Infringement?
Patent infringement occurs when an individual or entity violates one or more claims of a valid patent without the permission of the patent holder. This unauthorized use can take various forms, including manufacturing, selling, importing, or using the patented invention. For additional details refer to 35 U.S. Code § 271 – Infringement of Patent.
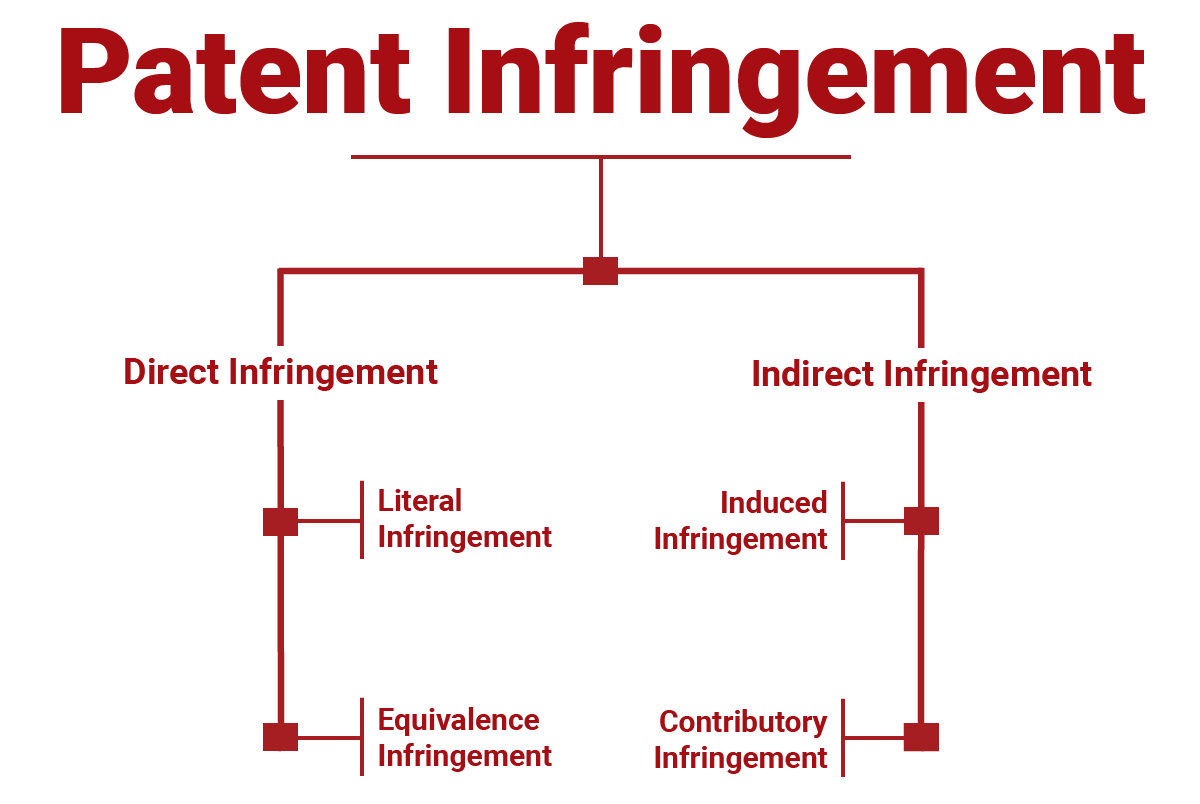
There are two primary types of patent infringement: literal infringement and infringement under the doctrine of equivalents. Literal infringement refers to a direct violation of the patented claims, while infringement under the doctrine of equivalents involves the use of an equivalent invention that performs substantially the same function as the patented invention.
Literal infringement requires a match between the accused product or process and the patented claims. On the other hand, infringement under the doctrine of equivalents allows for variations that still perform substantially the same function or achieve the same result as the patented invention. The doctrine of equivalents aims to prevent others from making minor changes to a patented invention to avoid infringement claims.
How to Identify Patent Infringement
Identifying patent infringement involves a detailed analysis of the patent claims and an understanding of their scope and limitations. Claim construction plays a crucial role in determining the boundaries of a patent and whether a potentially infringing product or process falls within those boundaries. Analysts will create claim charts to match the segments of a claim to aspects, components, and concepts within an infringing product.
To establish patent infringement, several elements must be satisfied, including the presence of a valid and enforceable patent, the accused product or process falling within the scope of the patent claims, and the absence of any valid defenses against infringement.
Examine real-world examples through the following case study, illustrating the process of identifying patent infringement, the challenges involved, and the strategies employed to determine infringement.
Case Study: Company A (Widget Co.) vs. Company B (Gadget Co.)
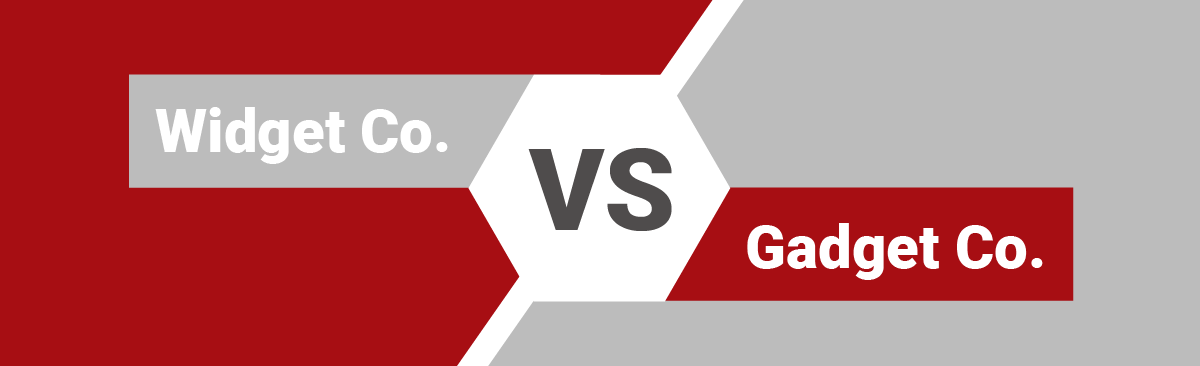
Widget Co. holds a patent for a unique widget design that improves efficiency in electronic devices. They suspect that Company B, a competitor, may be infringing on their patent with their latest product.
Understand the patent: Widget Co. reviews its patent documentation, focusing on the claims, description, and drawings. The patent claims describe the specific elements and features of their widget design that they believe are novel and inventive.
Analyze the product/process: Widget Co. examines Gadget Co’s product, specifically their latest widget model. They carefully study the product’s features, construction, and operation to determine if it matches their patented design.
Determine claim elements: Widget Co. identifies the essential elements of their patent claims, which include a specific arrangement of components, a unique circuitry configuration, and an innovative power-saving mechanism.
Assess infringement: Comparing Gadget Co’s widget with Widget Co.’s patent claims, Widget Co. discovers that Gadget Co’s widget has a similar arrangement of components and a power-saving mechanism, but the circuitry configuration is slightly different. Widget Co. consults with a patent attorney to assess the potential infringement.
Seek legal advice: Widget Co. engages a patent attorney specializing in intellectual property. The attorney reviews the patent claims, studies the products, and conducts a detailed analysis of the potential infringement. They determine that Gadget Co’s widget likely infringes Widget Co.’s patent because the differences in the circuitry configuration are minor and could be considered equivalents.
Legal action: Widget Co., with the assistance of their attorney, decides to pursue legal action against Gadget Co for patent infringement. They filed a lawsuit, claiming that Gadget Co’s widget infringes on their patented design, and seeks damages and an injunction to prevent further infringement.
Court proceedings: The case proceeds to court, where Widget Co. presents evidence, including patent documentation, product comparisons, and expert testimony. Gadget Co defends its product, arguing that it does not infringe on Widget Co.’s patent.
Ruling: The court carefully examines the patent claims, the accused product, and the arguments presented by both parties. The judge determines that Gadget Co’s widget infringes on Widget Co.’s patent because the circuitry configuration, although slightly different, performs substantially the same function in the same way. The court grants Widget Co. the requested damages and issues an injunction against Gadget Co’s infringing widget.
| Benefits of Patent Research and Analysis | Description |
| Identify potential infringement risks | Conducting patent research and analysis can help you identify potential patent infringement risks before launching a new product or service. By reviewing existing patents, you can determine whether your product or service may infringe on an existing patent, and make changes to avoid infringement. |
| Ensure patentability | Patent research and analysis can help you determine whether your invention is novel and non-obvious, which are requirements for obtaining a patent. By conducting a thorough patent search, you can identify any prior art that may affect the patentability of your invention, and make changes or modifications to increase the chances of obtaining a patent. |
| Enhance competitive intelligence | By reviewing the patents of competitors in your industry, you can gain valuable insights into their products and services, as well as their overall research and development strategy. This can help you identify potential areas for innovation, as well as areas where you may need to improve your own products or services to stay competitive. |
| Mitigate litigation risks | Conducting patent research and analysis can help you reduce the risk of patent litigation, which can be time-consuming and expensive. By identifying potential infringement risks and ensuring that your product or service is not infringing on any existing patents, you can reduce the likelihood of being sued for patent infringement. |
| Protect your own patents | By conducting regular patent research and analysis, you can monitor the patents of competitors and identify any potential infringement of your own patents. This can help you take action to protect your intellectual property and prevent others from profiting from your inventions. |
Defenses Against Patent Infringement
One common defense against patent infringement is the assertion of prior art, demonstrating that the accused invention existed before the filing date of the patent in question. Prior art can invalidate a patent or limit its scope, providing a defense for alleged infringers. Understanding the priority dates and a clear review of the claims and patent text are important aspects of this review.
Claiming patent invalidity is another defense against infringement. If a patent is proven to be invalid due to reasons such as lack of novelty, non-obviousness, or inadequate disclosure, the alleged infringer may escape liability.
Arguing non-infringement involves demonstrating that the accused product or process does not fall within the scope of the patent claims. This defense can be based on differences in functionality, design, or other factors that distinguish the accused invention from the patented invention.
Possible Consequences of Patent Infringement
Patent holders can seek civil remedies for patent infringement, including monetary damages, injunctive relief, and potential ongoing royalties. The severity of the penalties depends on various factors, such as the willfulness of the infringement, the extent of damages suffered by the patent holder, and the defendant’s financial resources.
In some cases, patent infringement can lead to criminal charges, particularly when intentional infringement and counterfeiting are involved. Criminal penalties may include fines and imprisonment, acting as a deterrent against willful infringement and protecting the integrity of the patent system.
Here are five notable patent infringement cases along with a brief summary of each:
Apple Inc. v. Samsung Electronics Co. (2012):
This high-profile case involved Apple accusing Samsung of infringing several design and utility patents related to smartphones and tablets. Apple claimed that Samsung’s devices, including the Galaxy series, copied the iPhone and iPad designs. The case went through multiple trials and appeals, resulting in judgments and settlements favoring both parties to some extent.
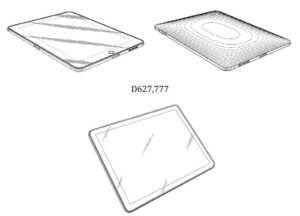
Source: ktMINE Search App
Oracle America, Inc. v. Google LLC (2016):
Oracle sued Google, alleging that Google’s use of certain Java APIs in the Android operating system infringed Oracle’s copyrights and patents. The case focused on whether the use of APIs constituted fair use. After multiple trials and appeals, the courts ruled in favor of Google, determining that their use of the APIs fell within fair use principles.
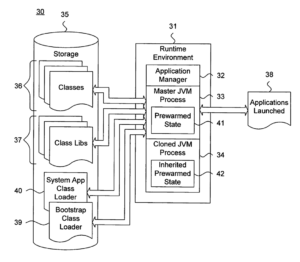
Source: ktMINE Search App
Merck & Co. v. Gilead Sciences, Inc. (2016):
Merck sued Gilead Sciences, alleging that Gilead’s hepatitis C drugs, Sovaldi and Harvoni, infringed on Merck’s patent related to a specific compound used to treat the disease. The case involved complex patent interpretation and validity issues. Ultimately, a jury ruled in favor of Merck, awarding them $2.5 billion in damages. However, the verdict was later overturned, and the case was remanded for a retrial.
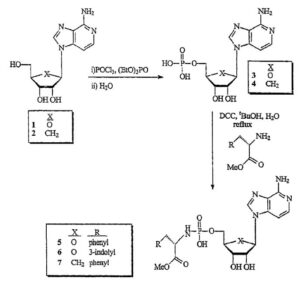
Source: ktMINE Search App
BlackBerry Limited v. Facebook, Inc. (2018):
BlackBerry filed a lawsuit against Facebook, alleging that various features within Facebook’s messaging services, including WhatsApp and Instagram, infringed on BlackBerry’s patents related to mobile messaging and notifications. The case focused on software patents and their interpretation. In 2020, the parties reached a settlement, the terms of which remain undisclosed.
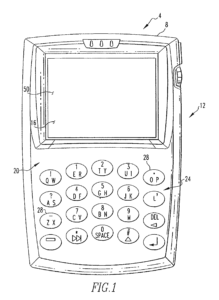
Source: ktMINE Search App
Lucent Technologies Inc. v. Microsoft Corp. (2007):
In this case, Lucent Technologies sued Microsoft for infringing on several patents related to audio coding technology used in the Windows operating system. The case involved complex technical arguments and damages calculations. Eventually, the jury ruled in favor of Lucent, awarding them $1.52 billion in damages. However, the verdict was later overturned, and the case was settled out of court with undisclosed terms.
These cases highlight the complexity and significance of patent infringement litigation, involving major technology companies and shaping legal interpretations in areas such as design, software, and pharmaceutical patents. It’s important to note that the outcomes of patent infringement cases can vary, and settlements are common, often resulting in undisclosed terms.
Source: ktMINE Search App
Using ktMINE for Patent Infringement Analysis
ktMINE’s platform offers robust patent research capabilities, providing access to an extensive database of patent information, including global patent filings, litigation records, and licensing agreements. The platform’s advanced search and analytics tools enable lawyers and law firms to conduct in-depth patent infringement analysis efficiently.
Using the Search App, users can easily search for similar patents using a wide range of fields such as Patent Owner, CPC Codes, Claims Text, and more. Once the robust search is performed, users can develop their case by reviewing full-text patents from over 70 jurisdictions. To also help with the value of damages, users can look at the patent royalty rates from similar patents right from the patent analytics pages.
The depth of the ktMINE platform from its data coverage and its analysis tools makes ktMINE an ideal product for evaluating patent data for infringement analysis. While patent data is important, ktMINE offers connected data tied to licensing, court cases, and other transactions that offer more depth to develop arguments about the impact the infringement has caused, while still allowing a review of the patent claims and text itself.
Importance of Comprehensive Patent Infringement Research for Lawyers and Law Firms
Comprehensive patent research is of utmost importance for lawyers specializing in intellectual property law for several key reasons:
Assessing patentability: Patent lawyers conduct extensive research to evaluate the patentability of an invention. By examining prior art, they can determine if the invention meets the criteria of novelty, non-obviousness, and industrial applicability. This research helps lawyers advise their clients on the likelihood of obtaining a patent and guides them in drafting strong patent applications.
Evaluating infringement risks: Patent research allows lawyers to assess the risk of patent infringement. By conducting a thorough analysis of existing patents and patent claims, lawyers can identify potential conflicts between their client’s products or services and existing patented technologies. This information helps lawyers advise clients on whether to proceed with their business activities, make design modifications, or seek licensing agreements to avoid legal disputes.
Supporting litigation strategies: In patent litigation cases, comprehensive patent research is essential for building a strong legal strategy. Lawyers need to analyze relevant patents and prior art to support their arguments concerning the infringement or validity of patents. By identifying prior art that anticipates or renders a patent obvious, lawyers can present strong evidence to challenge the validity of a patent or defend their clients against infringement claims.
Negotiating licensing agreements: Patent lawyers often play a crucial role in negotiating licensing agreements between patent holders and potential licensees. Through comprehensive patent research, lawyers can identify patents that align with their client’s business objectives or technologies. This research enables them to evaluate the scope of the patent rights, negotiate favorable licensing terms, and ensure their client’s compliance with existing patents.
Providing legal opinions: Clients often rely on patent lawyers to provide legal opinions regarding patent infringement or validity. Comprehensive patent research enables lawyers to conduct a thorough analysis of patents, prior art, and relevant legal precedents. Based on this research, lawyers can provide well-informed opinions on the strength of a patent, the likelihood of infringement, or the validity of a patent claim, assisting clients in making informed business decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding patent infringement is crucial for lawyers and law firms operating in the realm of intellectual property law. By utilizing ktMINE’s innovative platform, legal professionals can enhance their patent infringement research and analysis, identify strong defenses, and make informed decisions to protect their client’s rights. With ktMINE’s comprehensive data and powerful tools, lawyers and law firms can navigate the intricacies of patent infringement cases with confidence, ultimately contributing to a more robust and equitable intellectual property landscape.