What is Conductor ?
Last Updated :
13 Sep, 2023
Electric conductors are materials that allow electric charge to flow through their atomic structure as electrons. Insulators that obstruct the flow of electrons, and conductors allow the charged particles to move freely. The effectiveness of the conductor is measured with the help of its conductivity, which measures how quickly electrons may travel through the substance.

Electrical conductors
Above figure shows some of the examples of electrical conductors.
Comparison Between Resistance and Conductance in Conductor
|
It measures how much a material opposes the flow of electric current or charges.
| It is the reciprocal of resistance, and it measures the ease in the flow of charges through a material
|
It is measured in ohms (Ω).
| It is measured in Siemens (S) or mho.
|
Mathematically it can be defined as:
R= 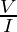
where,
R = resistance (ohm)
V= voltage (volts)
I = current (ampere)
| Mathematically it can be defined as:
G= 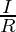
where,
G = conductance (S)
V= voltage (volts)
I = current (ampere)
|
Types of Conductor Materials
There are mainly three types of electric conductors:
- Metals
- Semiconductors
- Ionic Solutions
Metals
They are the type of substance which is characterized by their ability to conduct electricity. They are malleable and shiny in their appearance. They are found on the periodic table’s left side which include elements such as iron, copper, gold, aluminium, etc.
Important characteristics of Metals
- Conductivity: Metals have large number of free electrons which moves freely to conduct the electricity.
- Malleability: This means that metals can be easily beaten into thin sheets without breaking. They can be hammered, rolled, and stretched to form various shapes.
- Ductility: It means that the metals can be drawn into this wires without breaaking.
- Luster: It means shine. Metals have the property or ability to reflect light off their smooth surface.
- Melting and boiling points: Metals generally have high melting and boiling points due to strong metallic bonds between them.
Examples of Metals:
Some of the examples of metals are:
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Silver
- Gold
- Brass
- Iron
Semiconductors
A semiconductor is a type of material with qualities that are midway between those of conductors like metals and insulators like non-metals. They have distinct electrical behavior that makes them ideal for a wide range of electronic applications such as transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, etc. Semiconductors are of two types i.e. p-type ( majority charge carriers are holes) and n-type semiconductor (majority charge carriers are electrons) as seen in the figure below.

P and N type semiconductor
Important characteristics of Semiconductors
- Conductivity: Their conductivity is in between conductors and insulators. Their conductivity can be modified using doping.
- Doping: It means adding impurities into a semiconductor to improve or modify its electrical properties. There are two types of doping i.e. p-type or n-type.
- Temperature: Electric properties of a semiconductor depends on the temperature. When there is a rise in the temperature, the number of available electrons or holes increases which leads to a change in conductivity.
- Optical properties: Semiconductor materials can absorb and emit light at particular energy levels which makes them useful for the applications like LEDs and diodes.
Examples of Semiconductors:
Some of the examples of semiconductors are:
- Silicon
- Germanium
- Gallium Arsenide
Ionic Solutions
Ionic solutions are the solutions that contain ions and charged particles that dissolved in a solvent. They are also known as electrolyte solutions. The solution can conduct electricity due to the presence of the ions. These ions can move freely and can carry the electric charges. Ionic solution plays an important role in electrochemistry, biology and, material science.
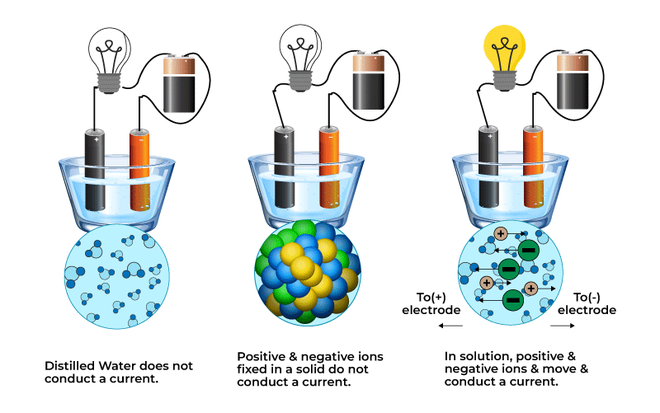
Different types of solutions
As seen in the above figure, distilled water (A) does not have any ions to conduct electricity. The second condition (B) has the ions, but they are fixed, hence do not conduct electricity. The last condition (C) has the free moving ions and hence the bulbs glow.
Important characteristics of Ionic Solutions
- Ions: They are the atoms or molecules with a net electric charge. Positively charged ions are known as cations, and negatively charged ions are known as anions.
- Conductivity: They are a good conductor of electricity because of the presence of free electrons or ions in a solution or electrolyte. Conductivity depends on the concentration of ions in the solution and their mobility.
- Ion dissociation: When an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent such as water, the positive and negative ions dissociate and gets surrounded by the water. This process is known as ionization.
Examples of Ionic Solutions:
Some of the examples of ionic solutions are:
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Skin Effect in Conductors
Skin effect is a phenomenon that occurs at high frequencies, where the distribution of electric charge or current become non-uniform. It means that the current near the surface is more as compared to the inside core of the material. This leads to less current flow inside the core. It is depicted in figure given below.
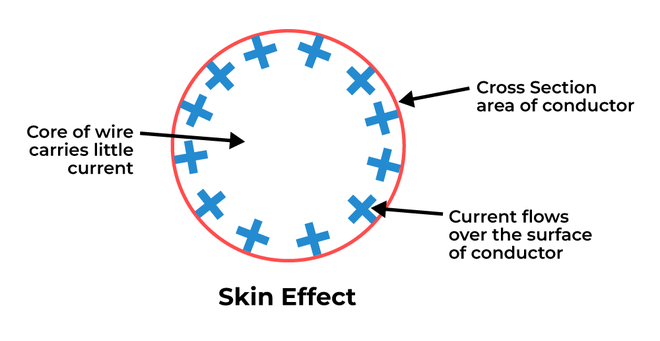
Skin effect in a Conductor
Causes of Skin Effect
It is caused by the interactions between the AC and the magnetic field generates around the conductor. As the frequency increase, the change in the magnetic field induces an opposing electric field within the conductor. This opposing electric field restricts current penetration into the interior of the conductor, causing the current to concentrate near the surface.
Key points
- Skin effect increases the effective resistance
- Higher the frequency, stronger the skin effect
- Non-uniform current distribution
To solve the problem caused by the skin effect, we can use conductors with larger diameters or hollow conductors.
Properties of Conductor
- Conductors allow electric charges to flow through them easily hence having high electrical conductivity and low resistivity.
- Many conductors can efficiently transfer heat through them. This property is called thermal conductivity.
- Conductors are malleable and ductile.
- Conductors like aluminum develop a protective oxide layer on their surface which helps them from corrosion. So conductors are corrosion resistant.
- Due to the mobility of their free electrons, conductors have electrochemical properties.
Advantages of Conductor
- It allows the efficient flow of electric current.
- It allows effective heat transfer.
- The voltage drop across the conductor is low which ensurs that the supply voltage remains the same.
- They can take part in electrochemical reactions because of the mobility of free electrons.
Disadvantages of Conductor
- Many conductors can corrode or oxidize when exposed to moisture which leads to the degradation in performance.
- Some conductors like gold and silver are very costly and increase the overall cost of the device despite of the fact that they are the best conductors.
- Heavy metals like copper, can be heavy and bulky. It can lead to a weight increment of the device.
- At high frequencies conductors can exhibit increased resistance due to the skin effect. So, this limits their application at a high frequency.
Applications of Conductor
There are lots of applications for conductors in the present world. Some of the applications are:
- Electric wiring
- Power transmission
- Motors and generators
- Heating elements
- Batteries
- Aerospace technology
- Antennas
FAQs on Conductor
Q.1: Why do we ground the conductors?
Answer:
Conductors are grounded to pass the electric charges into the ground, reducing the risk of electrical hazards and equipment damage.
Q.2: Why are gold and silver being used in the conductive device despite being very expensive than other metals?
Answer:
Gold and silver are being used because they have high conductivity and are corrosion resistant.
Q.3: What role is played by the crystal structure play in conductivity?
Answer:
The crystal structure affects how electrons can move freely within the material. Well-order crystal lattices tend to exhibit higher conductivity.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...