Linear resistors maintain constant resistance, following Ohm’s Law. Nonlinear resistors have varying resistance based on factors like temperature or voltage.
Linear vs Nonlinear Resistors
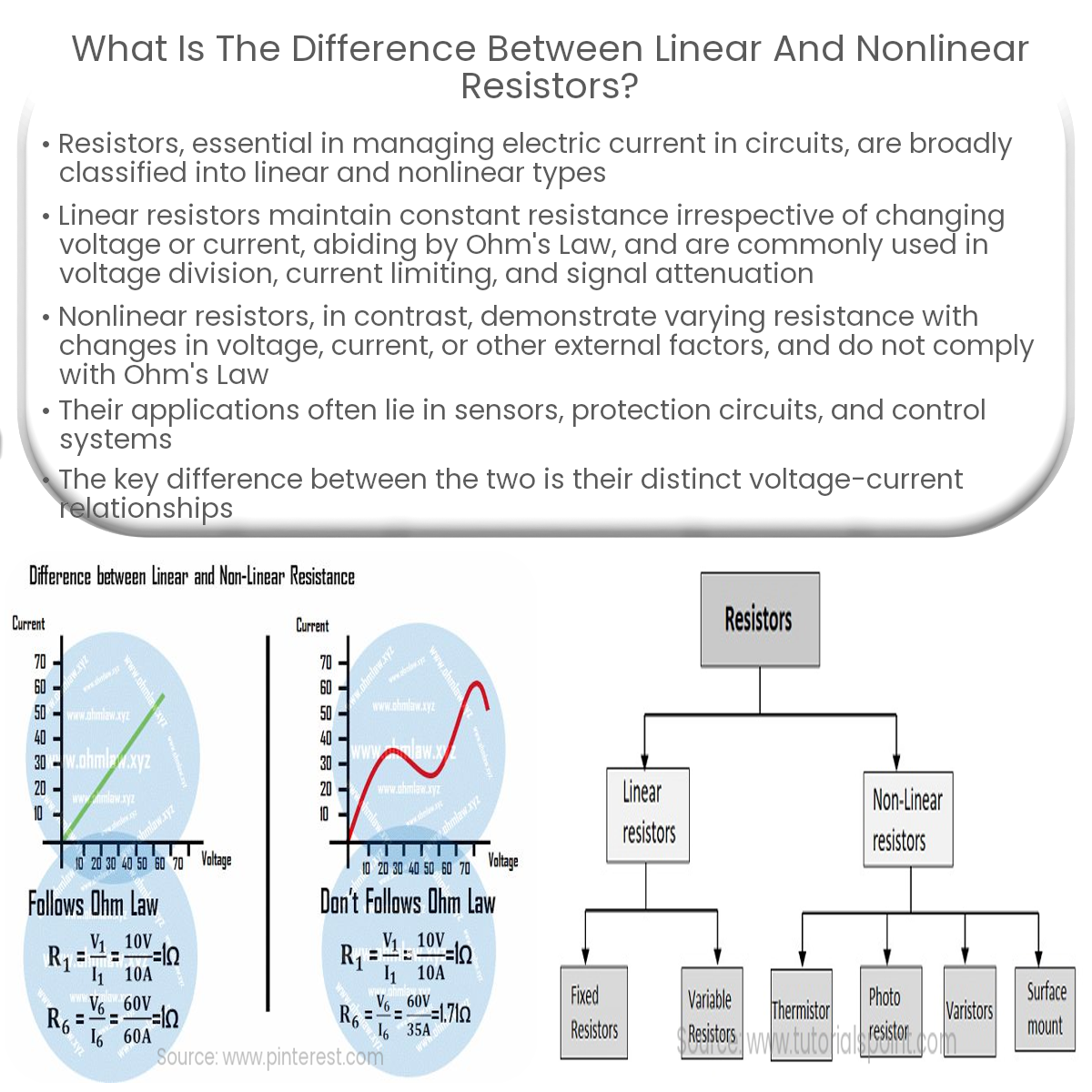
Resistors play an essential role in electronic circuits, managing the flow of electric current. They can be categorized into two main types: linear and nonlinear resistors. This article aims to explore the differences between these two types of resistors.
Linear Resistors
Linear resistors are those whose resistance remains constant as the voltage or current passing through them changes. In other words, they maintain a linear relationship between the voltage and current, adhering to Ohm’s Law, which states that V = IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
Examples of linear resistors include:
- Fixed resistors, which have a constant resistance value, are the most common type of linear resistors.
- Variable resistors, such as potentiometers and rheostats, allow for adjustments in resistance within a certain range.
Nonlinear Resistors
Nonlinear resistors, on the other hand, do not have a constant relationship between the voltage and current. Their resistance changes as the voltage or current applied to them varies, causing a nonlinear relationship between the two variables. Nonlinear resistors do not follow Ohm’s Law.
Examples of nonlinear resistors include:
- Thermistors, which are temperature-sensitive resistors. Their resistance changes with temperature, and they are available in two types: NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient).
- Varistors or voltage-dependent resistors (VDRs), which have a resistance that changes as the voltage applied to them changes. They are commonly used for overvoltage protection in electronic circuits.
- Photoresistors or light-dependent resistors (LDRs), which exhibit changes in resistance based on the amount of light incident on them.
Applications and Key Differences
Linear resistors are widely used in electronic circuits for various applications, including voltage division, current limiting, and signal attenuation. They are essential for ensuring stable, predictable performance in a circuit.
Nonlinear resistors find their applications in areas where resistance needs to vary based on specific conditions or parameters, such as temperature or voltage. They are often used in sensors, protection circuits, and control systems.
In summary, the main difference between linear and nonlinear resistors lies in their voltage-current relationship. Linear resistors maintain a constant resistance and adhere to Ohm’s Law, while nonlinear resistors exhibit a varying resistance based on external factors.