Explore the world of transistors – their fundamentals, types, applications, evolution, and profound impact on modern technology.

Understanding Transistors
When considering the fundamental components that make modern technology possible, transistors certainly stand at the forefront. A transistor is a critical element of almost every electronic device we use today, from computers and smartphones to advanced medical equipment and satellites.
In simple terms, a transistor is a type of semiconductor device primarily used for amplifying or switching electronic signals and electrical power. Conceived in 1947 at the Bell Laboratories by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, transistors have revolutionized the field of electronics and shaped the information age.
The Fundamentals of a Transistor
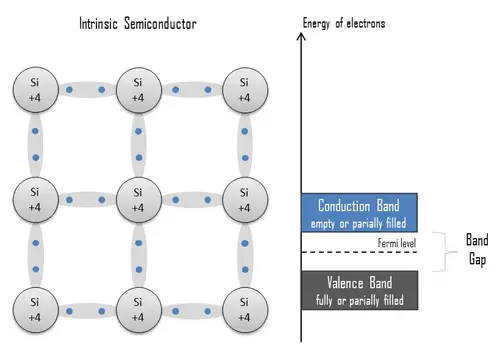
A transistor, at its core, consists of three layers of a semiconductor material. Each layer has a distinct name: the emitter, the base, and the collector. Depending on the application, the semiconductor material could either be a type of silicon or germanium, each doped or infused with impurities to control an electric charge.
- Emitter: This layer is heavily doped, meaning it has a high concentration of charge carriers (either free electrons or holes).
- Base: The base is lightly doped and very thin compared to the other layers. It serves as the main area for charge flow.
- Collector: This layer collects the charges that flow through the base from the emitter. It is moderately doped.
Types of Transistors
Transistors come in different types, primarily categorized into two groups based on their charge carrier type: NPN and PNP transistors.
- NPN Transistor: The emitter supplies electrons to the base while the collector collects the electrons from the base. Hence, the current flows from the collector to the emitter.
- PNP Transistor: The emitter supplies holes to the base, and the collector collects these holes. In this type, the current flows from the emitter to the collector.
These transistor types, with their ability to control the flow of electricity, have become an indispensable part of our everyday devices, playing a crucial role in processing information, driving signals, and managing power. The advent of transistors has, without a doubt, brought about the technological transformation that shapes our modern world.
[END OF PART ONE]
Applications of Transistors
Transistors are integral to a multitude of electronic devices due to their versatile functionalities. Some of their primary applications are:
- Amplification: Transistors are able to amplify a weak input signal into a strong output signal. This property is used in a variety of devices such as hearing aids, radio and television transmission, and audio amplification in public address systems.
- Switching: Transistors can be used as switches, rapidly turning a current on and off. This application is widely used in digital systems and computers, where binary language (1s and 0s) forms the basis of computation and data processing.
- Regulation of Electrical Signal: In voltage regulation applications, transistors are used to maintain constant output voltage levels, despite variations in input voltages or output load conditions. They play a critical role in power supply circuits.
The Evolution and Future of Transistors
Since their inception, transistors have undergone significant evolution, leading to substantial improvements in computational power. Moore’s Law, proposed by Gordon Moore in 1965, predicted that the number of transistors on a microchip would double approximately every two years. This prediction has held true for more than half a century, enabling advancements in microprocessor technology and digital electronics.
However, as transistor sizes approach the physical limits of miniaturization, researchers are exploring innovative technologies, such as quantum computing and carbon nanotubes, to take the technology to new heights.
Conclusion
In conclusion, transistors are fundamental building blocks of modern electronics and have profoundly impacted the evolution of technology. From amplifying signals to switching electronic states, they play an indispensable role in our everyday devices. Their ongoing development and future advancements promise to continue driving the digital age forward, making technology faster, more efficient, and capable of incredible computations. As we navigate through the 21st century, the transistor remains at the heart of the digital revolution, continuing to shape our world in ways unimaginable without this ingenious invention.