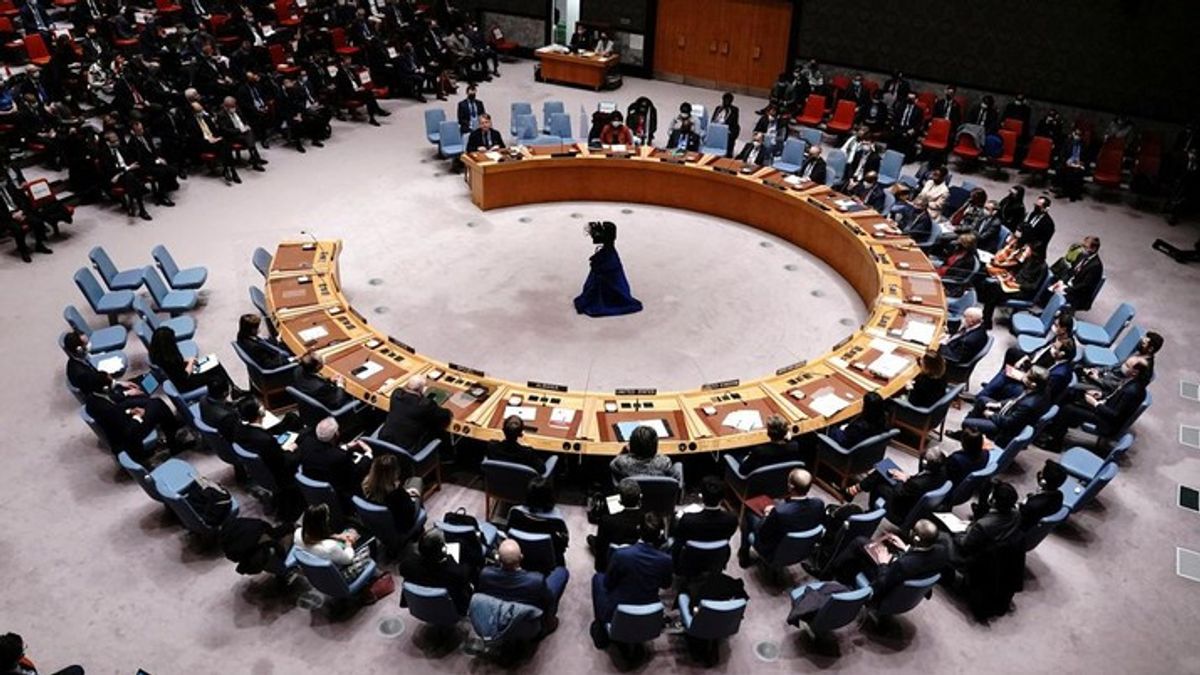
YOGYAKARTA - The United States is using veto rights to reject the UN Security Council (DK) proposal in calling for a ceasefire in Gaza. The decision was conveyed by the US at the UN DK meeting regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Apart from this Joe Biden-led country, there are several countries that have veto rights at the United Nations.
The UN DK meeting which was held on Friday (8/11) resulted in a resolution to peace in Gaza. The final determination of this resolution was carried out with the voting of 15 UN DK members. A total of 13 members agreed with the ceasefire resolution in the Israeli-Palestinian war.
The US is the only country that uses veto rights to reject ceasefire resolutions in Gaza. So which countries have veto rights at the United Nations and what are the provisions?
The veto rights of the UN Security Council are a privilege held by five Permanent Member States at UN DK. This veto right gives special voting powers to five UN countries to veto or cancel a proposed resolution at the United Nations.
This veto right as a special status arises as a result of the establishment of the United Nations after World War II. The winners of PD II, namely the US and the Soviet Socialist Republic, collaborated with Britain to form a political order after the war and establish the United Nations.
Franklin D Roosevelt, then US President, pushed the Republic of China (Taiwan) into part of the 'Global Police' in UNSC. Meanwhile Winston Churchill, British Prime Minister, encouraged France to continue to support Europe from the potential aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union while improving the status of its superpower.
The UN DK is currently filled with 15 member states, with 5 permanent member states as previously mentioned. The ten non-permanent member states of the UN DK do not have veto rights. These countries are Japan, Gabon, Brazil, Albania, Ghana, Ecuador, Malta, Mozambique, United Arab Emirates, and Switzerland.
There are five countries that have veto rights or privileges as permanent members of the UN DK. Five UN veto rights holders consist of China, the Russian Federation, France, the United States (US), and Britain.
The UN charter makers considered that the five countries had a key role in the establishment of the United Nations. In addition, the five countries also have important positions in maintaining international peace and security.
Five UN DK member states are given special authority in decision making or resolution at the United Nations. The designers agreed that if one of the member countries persists in voting negatively or rejection in DK which consists of 15 countries, the decision will not be approved.
The way the UN veto rights work is also considering other votes from UN DK members, totaling 15 countries if the rights of five permanent UN member states have used their veto rights at one time.
If there are permanent members who do not fully agree to a resolution or decision, but want to use veto rights then they can choose to abstain. This condition allows a resolution or decision to be adopted if you get nine votes in favor.
Based on the voting system as stated in Article 27 of the UN Charter, it is stated that:
SEE ALSO:
That's a review of a country that has veto rights at the United Nations and its authority. Despite its duty in overcoming international security threats, the use of UN veto rights has been criticized for often failing to represent many regions in the world.
Stay up to date with the latest domestic and other overseas news on VOI. We present the latest and most updated nationally and internationally.
The English, Chinese, Japanese, Arabic, and French versions are automatically generated by the AI. So there may still be inaccuracies in translating, please always see Indonesian as our main language. (system supported by DigitalSiber.id)