Documentary letter of credits in import/export business
A documentary credit in international trade represents an irrevocable commitment by the bank to pay the seller for goods or services. The amount of payment and time period are mentioned in credit documents. Documentary credits are and essential part in world trade today. It is a better way of securing and executing payments.
In case of DC, payment will be done only if the documents are as per the requirements. The bank decides to pay or not on the basis of the documents alone.
Documentary credit can also be used for other purposes like turnkey projects and periodically recurring commitments similar to guarantees.
Types of documentary credits by degree of security provided
Unconfirmed documentary credit
This documentary credit type is used commonly. The issuing bank must honor DC terms. Once this commitment has been entered into, the bank cannot decline responsibility without the beneficiary’s agreement. Thus, it is not possible to amend the DC unilaterally or cancel it.
In this case beneficiary must know where the credit is available. If available with the issuing bank, the beneficiary also considers the risk of mailing the documents. The beneficiary must know the deadline for delivering the documents to issuing bank.
The situation is different when the issuing bank authorizes another bank in a foreign country to honor and negotiate the documents in its place. In this event beneficiary’s bank can examine the documents and honor or negotiate on step-by-step basis but it is not obliged to do the same.
Confirmed Documentary Credit
When all the documents are given to Confirming bank or seller’s bank as per the instructions in DC, the confirming bank must honor or negotiate the payment or credit.
In case of confirmed DC beneficiary enjoys two independent recognitions of liability: one on the part of issuing bank and other on the part of confirming bank. However, some criteria’s must be fulfilled.
- The DC must clearly state that the issuing bank instructs the correspondent bank to give its confirmation.
- The DC must be available with confirming bank.
- The DC must be clear in its wording and there should not be conditions allowing buyer to take advantage.
Along with the basic technical considerations every bank will look into their credit policy and also evaluate credit and country risk before confirming. If the bank cannot confirm the DC, it may inform DC as unconfirmed to the issuing bank without delay.
Risk Involved:
With a confirmed DC, beneficiary seek payment from the bank which has committed on DC. If the issuing bank is also operating in beneficiary’s country than he will be re-lived from any country risk and risk of sending documents by mail.
The confirmed DC thus offers a very high degree of security.
A Credit must state the bank with which it is available. A credit available with a nominated bank is also available with the issuing bank. A credit must state whether it is available by sight payment, deferred payment, acceptance or negotiation.
Types of DCs by Payment Method
Sight DC
In this type of DC, beneficiary receives the payment after presentation and examination of the documents. This is a step by step process for payment against documents. A specific time period has been given to banks from the date of presentation of documents to inspect the documents.
Acceptance credit (DC with time draft)
In the case of acceptance credit, the seller sets a time limit or time draft on the issuing or confirming bank depending on the terms of credit. The payment date in acceptance credit may be, for example, 90 days after the invoice date or the date of shipment evidenced by the transport document. When the documents are presented, the draft is accepted instead of payment being made.
Deferred payment DC
In Deferred payment DCs, after presenting the proper documents, the authorized bank issues a written undertaking to make payment on due date. Due date is calculated on the basis of DC terms. Deferred payments are possible under both confirmed and unconfirmed DCs. Deferred payment DCs can be less expensive than DCs with time draft. The disadvantage compared with acceptance credit is that the prepayment of the amount due may normally be obtained only from the issuing or confirming bank (neither being obliged to make such pre-payment), whereas there are various possibilities of discounting a draft.
Acceptance credit and deferred payment DCs are financing instruments for the buyer. During the deferred payment period, the buyer can often sell the goods and use the money to pay the amount due under the DC.
Negotiable DC
These are either term or sight DCs and involve negotiation of the drafts/documents by the nominated bank. The payment has been done after presentation of either a draft plus prescribed documents or just the prescribed documents. The beneficiary receives the funds from nominated bank minus a discount charged by the negotiating bank.
The nominated bank transfers the fund after deducting the discount, either with recourse or without recourse. This has been done depending on whether the nominated bank did or did not confirm the DC or based on an agreement given to the beneficiary.
If the nominated bank has not confirmed the credit, it does not negotiate drafts/documents. Therefore, does not transfer the funds to beneficiary. In such cases it receives the drafts/documents and forwards them to the issuing bank. Bank will do the payment after they receive the funds from issuing bank.
Advance payment credit
Advanced payments can be secured and unsecured.
With secured advances, the bank of the beneficiary must provide a guarantee. The guarantee amount is normally reduced as the deliveries are made.
Unsecured advance payments do not give the importer any protection against misuse.
A special type of advance under a DC is the so called “red clause” credit. The clause gives some relief to the seller by giving some part of advance payment for procuring the material. This type of DC has been used in Australian wool trade.
As this clause was earlier written in red ink so it is called red clause. For example, read: “red clause AUD 50000 permitted”. This wording means that, nominated bank can give 50000 AUD to beneficiary as advance before presenting the actual documents. Such advance payments are made at the applicant’s risk.
Revolving credit
Many times, buyer needs to buy more goods than required to obtain better price. In such cases, delivery of the goods can be divided in to parts depending on the buyer’s requirement. Seller can ask buyer for revolving credit equivalent to cover the amount of part delivery.
For example, “credit amount: INR 10000, revolving 5 times to maximum INR 60000”. When first installment of INR 10000 has been drawn, it automatically becomes valid for next INR 10000. This can be done up to the limit max INR 60000. It is also possible to fix dates for the revolving credit installments.
Example of a confirmed DC
Documentary credit can take many different forms. The basic form of the credit is decided during the contract negotiations between the seller and the buyer. The terms of credit are decided when buyer asks his bank to issue the DC. At the same time seller has been informed by his bank about the terms of credit and he should make sure they are acceptable. If necessary, seller can ask buyer to change some terms or use precise wording in the terms.
It is necessary for both the parties to make sure the terms od DC transactions are clearly and correctly mentioned. This makes it easier to check the documents when the DC is utilized.
Contract
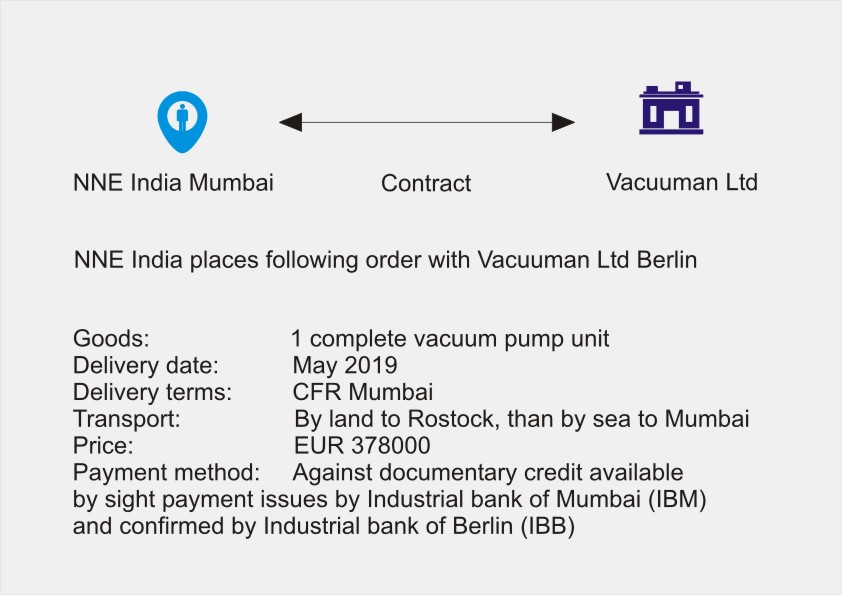
To make it easier to understand, following diagram will explain the documentary credit process used for confirmed credit. In our example, a vacuum pump is being supplied from Germany to India. Two banks are handling this DC operations. The Indian Bank (importer’s bank) and the German bank (exporter’s bank)
The Documentary Credit process can be carried out in two stages. First is issuing the DC and second is utilizing the DC.
Issuing (opening) the documentary credit
In our example, importers bank issues the DC on the request and instructions of Buyer. Before this buyer and seller have agreed upon the delivery and mode of payment. After receiving the buyer’s instruction, buyers bank checks if the necessary collateral or funds are available. Also bank check if there are any points to be clarified by client. After this the bank transmits the DC to seller’s bank or exporting country bank to confirm the DC. Also, at the same time they send advice notice to the buyer.
Process
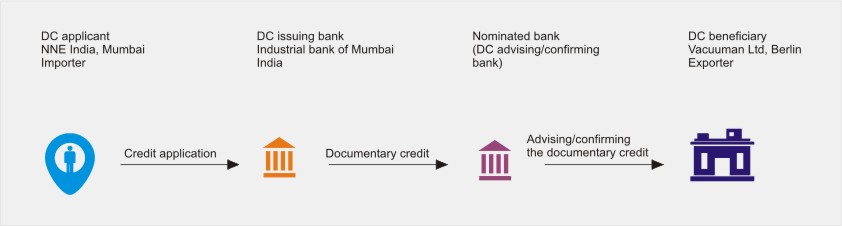
The bank in the seller’s country examines the content and of the DC and credit rating of the issuing bank in their home country. If everything is fine, they will confirm the DC. Also, they can refuse to confirm if it is not appropriate and inform to issuing bank.
Once seller receives the DC, he should check if there are any conditions which seller cannot meet. If there are any it should be immediately informed to buyer for making changes.
Using the Dc by presenting documents
Once the DC has been issued, the seller must present documents with in the time period mentioned in the DC. These also include transport documents which can be generated only after the shipment has been made. This is the evidence for the buyer that the seller has shipped the goods as agreed.
The seller will receive the payment after submitting the complete documents as per the terms and conditions mentioned in DC. The buyers bank will verify all the documents within time mentioned in the DC and credit the beneficiary’s account.
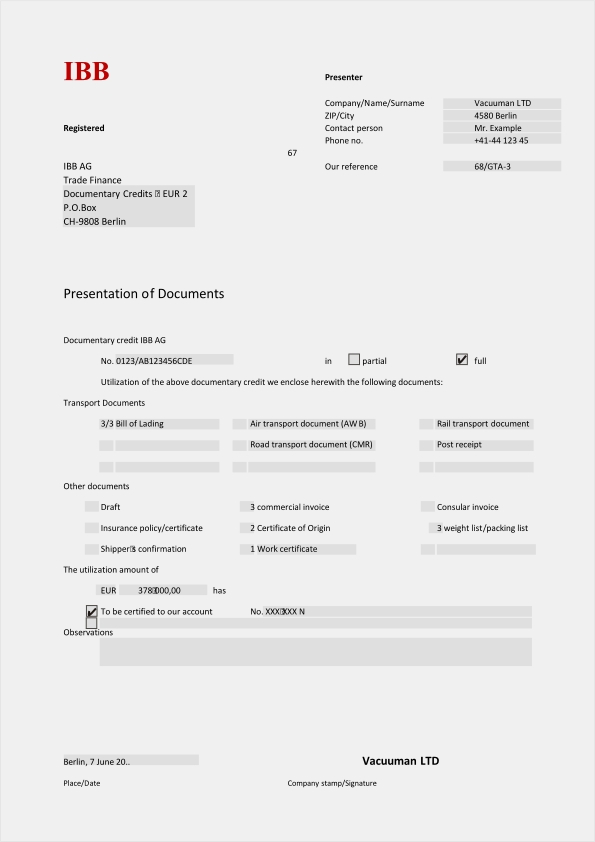
Documents presentation
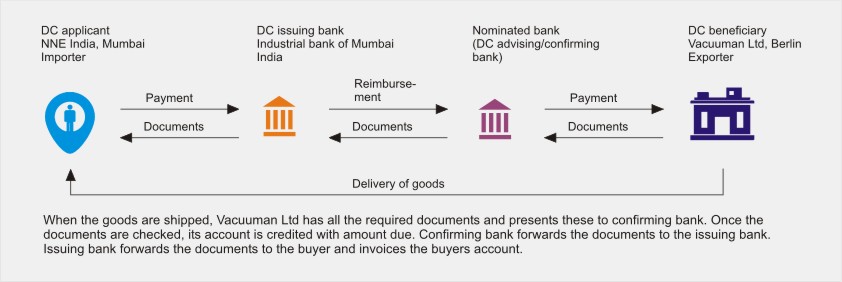
The confirming bank forwards the documents to the issuing bank. Also, the confirming bank debits the account of issuing bank or asks reimbursement form third bank. Third bank is called reimbursing bank. The reimbursing bank is the bank where both issuing and confirming bank have an account.
If the buyers bank founds documents not as per the DC terms, it can ask buyer for waiver of such discrepancies. This is also to be informed to the seller’s bank within the time period mentioned in the DC. Depending on the nature of discrepancies, proper corrective action to be taken by seller. In such cases bank can refuse to honor or negotiate the DC.
Important points for seller to consider while working with DC
Points to be checked before issuing DC.
- Seller should decide which type of DC will be most suitable before actual DC issuing. The seller should get confirmed DC by his own bank. This will give higher security against any type of risks. If sellers own bank is confirming DC, costs will be more but it will guarantee security.
- In order to avoid delay in Documentary Credit transactions, seller must ask to mention date before which he should get acceptable DC.
In order to avoid other disputes, seller must consider stating below points in DC.
- Amount and currency should be mentioned clearly.
- With regards to credit and quantity of goods, the seller should decide if he wants some flexibility by adding terms like approximately, percentage tolerance and plus or minus etc.
- Where can the documentary credit be utilized?
- Who is going to confirm DC?
- Is the DC transferable?
- Time deadlines to be checked like expiry date of DC, date of shipment of goods and presentation of documents.
- DC is at sight or deferred?
- Are partial shipments and transshipment to be allowed?
- What terms of delivery, places of shipment departure and destination are mentioned in DC?
- What documents to be presented on utilization? It has to be mentioned with all the details of documents.
- Which DC costs are to be borne by whom?

Points to check after the documentary credit has been issued.
- Check all the DC terms. If any terms not as per agreed by seller and buyer, request the buyer to change and have DC amended.
- Make sure to check all the terms and conditions. If you cannot fulfil all the terms and conditions, the bank security is lost.
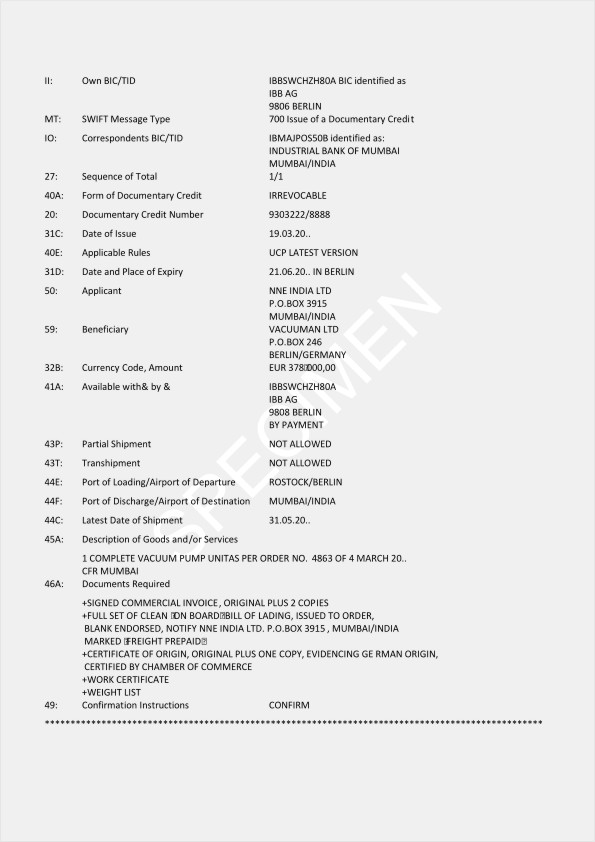
Points to check before documents are presented.
- The bank will transfer the funds only if the documents submitted are as per the DC in every respect. The bank cannot decide whether an irregularity in the documents is important or irrelevant.
Examination of documents generally includes checking the following points;
- Completeness
- Compliance with all the terms of the documentary credit
- Consistency of data content in a document and compared with other documents in DC
- Compliance with the rules of banking
Checking of terms related to timing.
Every DC must have expiry date. Also, it should have a time period for transport and presenting the documents to the bank. If these are not mentioned, bank will count 21 days from the date of shipment for presenting documents.
If the expiry date or last date of submission is on Sunday or holiday, the bank may accept documents on next working day.
If the expiry date of the DC is extended, it does not extend last day of shipment automatically. It has to be extended separately.
Expressions such as “prompt”, “immediately”, “as soon as”, and other similar should not be used in DC.
The expression “on or about” or similar will be considered as an event about to occur before or after mentioned period. In such cases both start and end dates are included.
The words “to”, “until”, “till”,” from” and “between” when used to determine the period of shipment include the date.
The words “from” and “after” when used to determine a maturity date exclude the date mentioned.
Terms such as “beginning of the month”, “first half of the month” and similar are considered as below:
Examples:
Fist half of the month: from 1st to 15th (inclusive) of the month
Second half of the month: from 16th to the last day (inclusive) of the month
Beginning of the month: from 1st to 10th (inclusive) of the month
Middle of the month: from 11th to 20th (inclusive) of the month
End of the month: from 21st to last day (inclusive) of the month
Points to check for Buyer in case of DC
The documentary credit is issued by the bank at the request of buyer. The buyer should consider the type of DC suitable for his needs. Also, the documents required to perform DC are important.
Buyer should consider following points while issuing DC.
- Buyer must mention whether the DC is confirmed by seller’s bank. If yes, buyer should also mention who is going to bear the cost of confirming DC. Buyer should give exact address of the seller who is to be beneficiary in order to avoid delays and errors. The amount of the credit and quantity of the goods may be specified accurately. It is advisable to keep some allowance with regards to the utilization of DC. If allowance is not specified, still seller can vary the quantity of goods by plus or minus 5%. But it cannot be done if prohibited.
- The place of presentation of documents and expiry date of DC must be fixed. Documentary Credit must specify the period of presentation of documents including original transport document after the date of shipment. If it is not mentioned and documents are presented after 21 days from the date of shipment, bank will reject the documents. In any case it has to be presented before the expiry of the DC.
- Buyer should specify shipping period and whether partial shipment or transshipment are allowed.
- Buyer should clearly mention which documents are required. Documents type will be generally depending on the means of transport, type of goods and delivery term.
- Buyer should avoid terms which can complicate the processing of the credit or difficult to fulfill.
- If issuing bank, confirming bank (if any) and buyer agree to change credit than it is possible.

Costs
Bank charges commission and fees for issuing and amending Documentary Credits. These are for covering risks associated with credit, given credit and time spent on DC.
Charges and fees when issuing the DC:
- Opening fees
- The commitment fee, which is charges from the date of issue to the date of payment.
When advising the DC of correspondent bank:
- The advising commission for advising credit without confirmation
Charges when confirming the DC of correspondent bank:
- Advising commission
- The confirmation commission, which is calculated from the date of confirmation to the date of payment.
When amending the DC:
- The fees for making the amendment
When the documentary credit is processed:
- The payment commission for checking the documents and making the payment.
- The acceptance commission for accepting time drafts.

Pingback: Securing performance risks and payment in foreign trade - NNE