abnormal occlusion
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Encyclopedia.
occlusion
[ŏ-kloo´zhun]1. obstruction.
2. the trapping of a liquid or gas within cavities in a solid or on its surface.
3. the relation of the teeth of both jaws when in functional contact during activity of the mandible.
4. momentary complete closure of some area in the vocal tract, causing breathing to stop and pressure to accumulate.

Normal occlusion of the primary molars. From Darby and Walsh, 1994.
abnormal occlusion malocclusion.
central occlusion (centric occlusion) occlusion of the teeth when the mandible is in centric relation to the maxilla, with full occlusal surface contact of the upper and lower teeth in habitual occlusion.
coronary occlusion see coronary occlusion.
eccentric occlusion occlusion of the teeth when the lower jaw has moved from the centric position.
functional occlusion contact of the maxillary and mandibular teeth that provides the highest efficiency in the centric position and during all exclusive movements of the jaw that are essential to mastication without producing trauma.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
ab·nor·mal oc·clu·sion
an arrangement of the teeth that is not considered to be within the normal range of variation.
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
ab·nor·mal oc·clu·sion
(ab-nōr'măl ŏ-klū'zhŭn)An arrangement of the teeth that is not considered to be within the normal range of variation.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012
occlusion
(o-kloo'zhun) [L. occlusio, a closing up]1. The acquired or congenital closure, or state of being closed, of a passage. Synonym: imperforation
2. Alignment of the mandibular and maxillary teeth when the jaw is closed or in functional contact. Synonym: dental occlusion See: malocclusion
3. The covering of an eye in order to improve vision in the other, e.g., in treating strabismus.
acquired centric occlusion
Centric occlusion.abnormal occlusion
Malocclusion.adjusted occlusion
See: equilibrationanatomical occlusion
In dentistry, an occlusion in which the posterior teeth of a denture have masticatory surfaces that resemble natural, healthy dentition and articulate with the surfaces of similar or opposing teeth. The opposing teeth may be artificial or natural.
arterial occlusion
A blockage of blood flow through an artery. It may be acute or chronic and occurs, for example, in coronary or in peripheral arteries. Patients with acute arterial occlusion have severe pain (as in angina pectoris), decreased or absent pulses, and mottling of the skin of an affected extremity. The occlusion is removed and blood flow restored if possible.
balanced occlusion
The ideal and equal contact of the teeth of the working side of the jaw by the complementary contact of the teeth on the opposite side of the jaw. Synonym: balanced bite
central retinal artery occlusion
Abbreviation: CRAOBlockage of blood flow to the retina (that is, to the central retinal artery or one of its branches), resulting in sudden visual loss. The condition usually affects one eye. When the retinal artery is blocked by a blood clot, early thrombolysis sometimes provides sight-preserving therapy.
Etiology
CRAO is typically caused by a tiny embolus that lodges in the retinal circulation. It usually occurs in people with high blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, cardiac valve disease, or atrial fibrillation, which predispose to atherosclerosis or arterial embolization. Other causes include inflammatory or autoimmune diseases affecting the circulation (arteritis), clotting disorders, hyperlipidemia, injected drugs or contaminants, and tumor metastases.
centric occlusion
In dentistry, the vertical and horizontal position of the mandible that produces maximal interdigitation of the cusps of the maxillary and mandibular teeth. This is the ideal position or type of occlusion. Synonym: acquired centric occlusion; habitual centric occlusion; intercuspal position
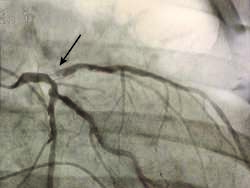
coronary occlusion
Complete or partial obstruction of a coronary vessel by thrombosis or as a result of spasm. Synonym: cardiac thrombosis; coronary thrombosis
See: myocardial infarction; illustrationdental occlusion
Occlusion (2).eccentric occlusion
Any dental occlusion other than centric.
habitual occlusion
The usual relationship between the teeth of the maxilla and mandible that represents the maximum contact. This occlusion varies from person to person and is seldom ideal or true centric occlusion.
habitual centric occlusion
Centric occlusion.occlusion of the pupil
In the eye, a pupil with an opaque membrane shutting off the pupillary area.
traumatic occlusion
Injury to the tissues that support the teeth because of malocclusion, missing teeth, improper chewing habits, or a pathological condition that causes a person to chew abnormally.
working occlusion
The usual method of contact of teeth as the mandible is moved to one side during chewing.
Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners
ab·nor·mal oc·clu·sion
(ab-nōr'măl ŏ-klū'zhŭn)Arrangement of teeth not considered to be within normal range of variation.
Synonym(s): abnormal occlusal relationship.
Synonym(s): abnormal occlusal relationship.
Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions © Farlex 2012