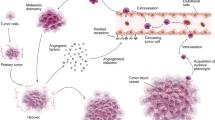
Abstract
The growth of blood vessels from already existing vasculature is angiogenesis and it is one of the fundamental processes in fetal development, tissue damage or repair, and the reproductive cycle. In a healthy person, angiogenesis is regulated by the balance between pro- and anti-angiogenic factors. However, when the balance is disturbed, it results in various diseases or disorders. The angiogenesis pathway is a sequential cascade and differs based on the stimuli. Therefore, targeting one of the factors involved in the process can help us find a therapeutic strategy to treat irregular angiogenesis. In the past three decades of cancer research, angiogenesis has been at its peak, where an anti-angiogenic agent inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a promising substance to treat cancer. In addition, cancer can be assessed based on the expression of angiogenic factors and its response to therapies. Angiogenesis is important for all tissues, which might be normal or pathologically changed and occur through ages. In clinical therapeutics, target therapy focusing on discovery of novel anti-angiogenic agents like bevacizumab, cetuximab, sunitinib, imatinib, lenvatinib, thalidomide, everolimus etc., to block or inhibit the angiogenesis pathway is well explored in recent times. In this review, we will discuss about the molecular signaling pathways involved in major angiogenic diseases in detail.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Lenzi P, Bocci G, Natale G (2016) John Hunter and the origin of the term “angiogenesis” medicine. Angiogenesis 19(2):255–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-016-9496-7
Ausprunk DH, Folkman J (1977) Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res 14(1):53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8
Caduff JH, Fischer LC, Burri PH (1986) Scanning electron microscope study of the developing microvasculature in the postnatal rat lung. Anat Rec 216(2):154–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092160207
Chung AS, Ferrara N (2011) Developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:563–584. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154002
Andrea U, Thomas W, Paolo V, Maggio D, Matteo P, Lorenz G, Andrea B, Roberto G (2019) Vascular endothelial growth factor biology for regenerative angiogenesis. Swiss Med Wkly 149:w20011. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2019.20011
Ferrara N (2001) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in regulation of physiological angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(6):C1358–C1366. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.2001.280.6.C1358
Sasaki K, Kiuchi Y, Sato Y, Yamamori S (1991) Morphological analysis of neovascularization at early stages of rat splenic autografts in comparison with tumor angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 265:503–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340873
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A, Vincenti V, Compernolle V, De Mol M, Wu Y, Bono F, Devy L, Beck H, Scholz D, Acker T, Dipalma T, Dewerchin M, Noel A, Stalmans I, Barra A, Blacher S, Vandendriessche T, Ponten A, Eriksson U, Plate KH, Foidart JM, Schaper W, Charnock-Jones DS, Hicklin DJ, Herbert JM, Collen D, Persico MG (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7(5):575–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/87904
Huang Z, Bao SD (2004) Roles of main pro- and anti-angiogenic factors in tumor angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 10(4):463–470. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i4.463
St. Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, Traverso G, Romans KE, Montegomery E, Lal A, Riggins GJ, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (2000) Genes expressed in human tumor endothelium. Science 289(5482):1197–1202. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5482.1197
Seaman S, Stevens J, Yang MY, Logsdon D, Graff-Cherry C, St Croix B (2007) Genes that distinguish physiological and pathological angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 11(6):539–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2007.04.017
Simons M (2004) Integrative signaling in angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 264:99–102
Gore AV, Swift MR, Cha YR, Lo B, Mckinney MC, Li W, Castranova D, Davis A, Mukouyama Y, Weinstein BM (2011) Rspo1/Wnt signaling promotes angiogenesis via Vegfc/Vegfr3. Development 138:4875–4886. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.068460
Jiang BH, Liu LZ (2008) PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784(1):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.008
Ushio-Fukai M (2006) Redox signaling in angiogenesis: role of NADPH oxidase. Cardiovasc Res 71(2):226–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.04.015
Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Kinnaird A, Stenson TH, Haromy A, Parker JMR, Mcmurtry MS, Michelakis ED (2013) Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1 a signaling and angiogenesis in cancer. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.198
Ikeda H, Kakeya H (2021) Targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) signaling with natural products toward cancer chemotherapy. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 74(10):687–695. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-021-00451-0
Ritvo M (1960) The role of diagnostic roentgenology in medicine. N Engl J Med 262(24):1201–1209. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm196006162622401
Muthakkaruppan VR, Kubai L, Auerbach R (1982) Tumor-induced neovascularization in the mouse eye. J Natl Cancer Inst 69(3):699–708. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/69.3.699
Dameron KM, Volpert OV, Tainsky MA, Bouck N (1994) Control of angiogenesis in fibroblasts by p53 regulation of thrombospondin-1. Science 265(5178):1582–1584. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7521539
Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T, Kojiro M (2006) Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2(3):213–219. https://doi.org/10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.213
Lugano R, Ramachandran M, Dimberg A (2020) Tumor angiogenesis : causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci 77(9):1745–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03351-7
Pucci C, Martinelli C, Ciofani G (2019) Innovative approaches for cancer treatment: current perspectives and new challenges. Ecancermedicalscience 13:961. https://doi.org/10.3332/ecancer.2019.961
Irshad I, Varamini P (2018) Different targeting strategies for treating breast cancer bone metastases. Curr Pharm Des 24(28):3320–3331. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612824666180619165728
Azad T, Ghahremani M, Yang X (2019) The role of YAP and TAZ in angiogenesis and vascular mimicry. Cells 8(5):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050407
Neuzillet C, De Gramont A, Tijeras-Raballand A, De Mestier L (2014) Perspectives of TGF-β inhibition in pancreatic and hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncotarget 5(1):78–94. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1569
Donovan D, Harmey JH, Toomey D, Osborne DH, Redmond HP, Bouchier-Hayes DJ (1997) TGF beta-1 regulation of VEGF production by breast cancer cells. Ann Surg Oncol 4(8):621–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02303745
Neuzillet C, Cohen R (2015) Targeting the TGFβ pathway for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther 147:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.11.001
Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Lavezzari G, Antonaci S, Giannelli G (2009) Inhibition of transforming growth factor β receptor I kinase blocks hepatocellular carcinoma growth through neo-angiogenesis regulation. Hepatology 50(4):1140–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23118
Ito N, Kawata S, Tamura S, Shirai Y, Kiso S, Tsushima H, Matsuzawa Y (1995) Positive correlation of plasma transforming growth factor-beta 1 levels with tumor vascularity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 89(1):45–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3835(95)90156-6
Zhang M, Herion TW, Timke C, Han N, Hauser K, Weber KJ, Peschke P, Wirkner U, Lahn M (2011) Trimodal glioblastoma treatment consisting of concurrent radiotherapy, temozolomide, and the novel TGF-β receptor I kinase inhibitor LY21097611,2. Neoplasia 13(6):537–549. https://doi.org/10.1593/neo.11258
Zhang M, Kleber S, Röhrich M, Timke C, Han N, Tuettenberg J, Martin-Villalba A, Debus J, Peschke P, Wirkner U, Lahn M, Huber PE (2011) Blockade of TGF-β signaling by the TGFβR-I kinase inhibitor LY2109761 enhances radiation response and prolongs survival in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 71(23):7155–7167. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1212
Akbari A, Amanpour S, Muhammadnejad S, Ghahremani MH, Ghaffari SH, Dehpour AR, Mobini GR, Shidfar F, Abastabar M, Khoshzaban A, Faghihloo E, Karimi A, Heidari M (2014) Evaluation of antitumor activity of a TGF-beta receptor i inhibitor (SD-208) on human colon adenocarcinoma. DARU J Pharm Sci 22(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-22-47
Goel HL, Mercurio AM (2013) VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer 13(12):871–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3627
Schmidt NO, Westphal M, Hagel C, Ergün S, Stavrou D, Rosen EM, Lamszus K (1999) Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in human gliomas and their relation to angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 84(1):10–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19990219)84:1%3c10::AID-IJC3%3e3.0.CO;2-L
Trejo-solís C, Pedraza-chaverrí J, Torres-ramos M, Jiménez-farfán D, Salgado AC, Serrano-garcía N, Osorio-rico L, Sotelo J (2013) Multiple molecular and cellular mechanisms of action of lycopene in cancer inhibition. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:705121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/705121
Guo D, Murdoch CE, Liu T et al (2018) Therapeutic angiogenesis of Chinese herbal medicines in ischemic heart disease: a review. Front Pharmacol 9:428. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.0042862
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I, Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Lu KV, Yoshimoto K, Huang JHY, Chute DJ, Riggs BL, Horvath S, Liau LM, Cavenee WK, Rao PN, Beroukhim R, Peck TC, Lee JC, Sellers WR, Stokoe D, Prados M, Cloughesy TF, Sawyers CL, Mischel PS (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353(19):2012–2024. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa051918
Rao MA, Cooley HJ (1995) Rates of structure development during gelation and softening of high-methoxyl pectin—sodium alginate—fructose mixtures. Top Catal 9(4):229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0268-005X(09)80253-1
Waugh DJJ, Wilson C (2008) The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(21):6735–6741. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4843
Pao W, Chmielecki J (2010) Rational, biologically based treatment of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10(11):760–774. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2947
Minder P, Zajac E, Quigley JP, Deryugina EI (2015) EGFR regulates the development and microarchitecture of intratumoral angiogenic vasculature capable of sustaining cancer cell intravasation. Neoplasia 17(8):634–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2015.08.002
Heldin CH, Westermark B (1999) Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol Rev 79(4):1283–1316. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1999.79.4.1283
Dietrich J, Diamond EL, Kesari S (2010) Glioma stem cell signaling: therapeutic opportunities andchallenges. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10(5):709–722. https://doi.org/10.1586/era.09.190
Cao Y, Cao R, Hedlund EM (2008) R Regulation of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by FGF and PDGF signaling pathways. J Mol Med (Berl) 86(7):785–789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0337-z
Oumesmar BN, Vignais L, Baron-Van Eyercooren A (1997) Developmental expression of platelet-derived growth factor α-receptor in neurons and glial cells of the mouse CNS. J Neurosci 17(1):125–139. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.17-01-00125.1997
Westermark B, Heldin C-H, Nistér M (1995) Platelet-derived growth factor in human glioma. Glia 15(3):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.440150307
Dai C, Celestino JC, Okada Y, Louis DN, Fuller GN, Holland EC (2001) PDGF autocrine stimulation dedifferentiates cultured astrocytes and induces oligodendrogliomas from and oligoastrocytomas neural progenitors and astrocytes in vivo. Genes Dev 15(15):1913–1925. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.903001
Taeger J, Moser C, Hellerbrand C, Mycielska ME, Glockzin G, Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK, Stoeltzing O, Lang SA (2011) Targeting FGFR/PDGFR/VEGFR impairs tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis by effects on tumor cells, endothelial cells, and pericytes in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 10(11):2157–2167. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0312
Gavalas NG, Liontos M, Trachana SP, Bagratuni T, Arapinis C, Liacos C, Dimopoulos MA, Bamias A (2013) Angiogenesis-related pathways in the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14(8):15885–15909. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140815885
Turner N, Grose R (2010) Fibroblast growth factor signaling: from development to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 10(2):116–129. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2780
Korc M, Friesel R (2009) The role of fibroblast growth factors in tumor growth. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9(5):639–651. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800909789057006
Touat M, Ileana E, Postel-Vinay S, André F, Soria JC (2015) Targeting FGFR signaling in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21(12):2684–2694. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2329
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2003) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 9(6):677–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0603-677
Brugarolas J, Lei K, Hurley RL, Manning BD, Reiling JH, Hafen E, Witters LA, Ellisen LW, Kaelin WG Jr (2004) Regulation of mTOR function in response to hypoxia by REDD1 and the TSC1/TSC2 tumor suppressor complex. Genes Dev 18(23):2893–2904. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1256804
Jiang BH, Jiang G, Zheng JZ, Lu Z, Hunter T, Vogt PK (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell Growth Differ 12(7):363–369
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J, Semenza GL, Van Obberghen E (2002) Insulin stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor 1 through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/target of rapamycin-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277(31):27975–27981. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204152200
Arai M, Kawachi T, Sato H, Setiawan A, Kobayashi M (2014) Marine spongian sesquiterpene phenols, dictyoceratin-C and smenospondiol, display hypoxia-selective growth inhibition against cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24(14):3155–3157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.04.116
Ahmed Z, Bicknell R (2009) Angiogenic signaling pathways. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 467:3–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-241-0_1
Pate KT, Stringari C, Sprowl-tanio S, Wang K, Teslaa T, Hoverter NP, Mcquade MM, Garner C, Digman MA, Teitell MA, Edwards RA, Gratton E, Waterman ML, Pate KT (2014) Wnt signaling directs a metabolic program of glycolysis and angiogenesis in colon cancer. EMBO J 33(13):1454–1473. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201488598
Kohn AD, Moon RT (2005) Wnt and calcium signaling: β-catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium 38(3–4):439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.022
Manandhar S, Kabekkodu SP, Pai KSR (2020) Aberrant canonical Wnt signaling: phytochemical based modulation. Phytomedicine 76:153243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153243
Sa B, Moreno S, Cabello J (2013) Multiple functions of the noncanonical Wnt pathway. Trends Genet. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2013.06.003
Goodwin AM, D’Amore PA (2002) Wnt signaling in the vasculature. Angiogenesis 5(1–2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1021563510866
Lyle CL, Belghasem M, Chitalia VC (2019) c-Cbl: an important regulator and a target in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Cells 8(5):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050498
Klaus A, Birchmeier W (2008) Wnt signaling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8(5):387–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2389
Jiang BH, Liu LZ (2008) PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics 1784(1):150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.008
Dibbens JA, Miller DL, Damert A, Risau W, Vadas MA, Goodall GJ (1999) Hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA stability requires the cooperation of multiple RNA elements. Mol Biol Cell 10(4):907–919. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.10.4.907
Jiang BH, Zheng JZ, Aoki M, Vogt PK (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling mediates angiogenesis and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(4):1749–1753. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.040560897
Thomas C, Lamoureux F, Crafter C, Thomas C, Lamoureux F, Crafter C, Davies BR, Beraldi E, Fazli L (2013) Synergistic targeting of PI3K/AKT pathway and androgen receptor axis significantly delays castration-resistant prostate cancer progression in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 12(11):2342–2355. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0032
Huang D, Ding Y, Luo W, Bender S, Qian C, Kort E, Zhang Z, Vandenbeldt K, Duesbery NS, Resau JH, Teh BT (2008) Inhibition of MAPK kinase signaling pathways suppressed renal cell carcinoma growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res 68(1):81–88. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5311
Aguzzi A, Maggioni D, Nicolini G, Tredici G, Gaini RM, Garavello W (2009) MAP kinase modulation in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Anticancer Res 29(1):303–308
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD, Whitmarsh AJ (2013) MAP kinase signaling cascades and transcriptional regulation. Gene 513(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.10.033
Wong K (2014) The therapeutic promise of anti-cancer drugs against the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Top Anti-Cancer Res 2:63–94
Kato Y, Tapping RI, Huang S, Watson MH, Ulevitch RJ, Lee JD (1998) Bmk1/Erk5 is required for cell proliferation induced by epidermal growth factor. Nature 395(6703):713–716. https://doi.org/10.1038/27234
Gkouveris I, Nikitakis N, Karanikou M, Rassidakis G, Sklavounou A (2016) JNK1/2 expression and modulation of STAT3 signaling in oral cancer. Oncol Lett 12(1):699–706. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4614
Mishima K, Inoue K, Hayashi Y (2002) Overexpression of extracellular-signal regulated kinases on oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 38(5):468–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1368-8375(01)00104-x
Peng Q, Deng Z, Pan H, Gu L, Liu O, Tang Z (2018) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in oral cancer. Oncol Lett 15(2):1379–1388. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7491
Ensoli B, Markham P, Kao V, Barillari G, Fiorelli V, Gendelman R, Raffeld M, Zon G, Gallo RC (1994) Block of AIDS-Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) cell growth, angiogenesis, and lesion formation in nude mice by antisense oligonucleotide targeting basic fibroblast growth factor. A novel strategy for the therapy of KS. J Clin Investig 94(5):1736–1746. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI117521
Barillari G, Ensoli B (2002) Angiogenic effects of extracellular human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein and its role in the pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Clin Microbiol Rev 15(2):310–326. https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.15.2.310-326.2002
Burgess WH, Maciag T (1989) The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 58(1):575–602. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043
Xerri L, Hassoun J (1991) Fibroblast growth factor gene expression in in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol 138(1):9–15
Martellotta F, Berretta M, Vaccher E, Schioppa O, Zanet E, Tirelli U (2009) AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma: state of the art and therapeutic strategies. Curr HIV Res 7(6):634–638. https://doi.org/10.2174/157016209789973619
Bullock J, Rizvi AA, Saleh AM, Ahmed S (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med Princ Pract 27(6):501–507. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493390
Kokkonen H, Söderström I, Rocklöv J, Hallmans G, Lejon K, Rantapää Dahlqvist S (2010) Up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62(2):383–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27186
Dulak J, Jozkowicz A, Łoboda A (2013) Angiogenesis Vascularisation: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Health and Diseases. Springer, Wien, Heidelberg, New York, Dordrecht, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1428-5
Elshabrawy HA, Chen Z, Volin MV, Ravella S, Virupannavar S, Shahrara S (2015) The pathogenic role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Angiogenesis 18(4):433–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-015-9477-2
Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, van de Loo FA, van den Berg WB (2011) Trapped in a vicious loop: toll-like receptors sustain the spontaneous cytokine production by rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Res Ther 13(2):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3287
Murphy G, Knäuper V, Atkinson S, Butler G, English W, Hutton M, Stracke J, Clark I (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in arthritic disease. Arthritis Res 4(Suppl 3):S39–S49. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar572
Szekanecz Z, Vegvari A, Szabo Z, Koch AE (2010) Chemokines and chemokine receptors in arthritis. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2:153–167. https://doi.org/10.2741/s53
De SF, Maria L, Aires R, Lima C, Aires F, Lima C, Barcelos G, Freire J, Carvalho D (2010) Autoimmunity reviews the Wnt signaling pathway and rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 9(4):207–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2009.08.003
Yuan FL, Li X, Lu WG, Sun JM, Jiang DL, Xu RS (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) as a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 32(3):289–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2119-9
Rosengren S, Corr M, Boyle DL (2010) Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor beta synergistically potentiate inflammatory mediator synthesis by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 12(2):R65. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2981
Ciobanu DA, Poenariu IS, Crînguș L, Vreju FA, Turcu-stiolica A, Tica AA, Padureanu V, Dumitrascu RM, Banicioiu-covei S, Dinescu SC, Boldeanu L, Siloși I, Ungureanu AM, Boldeanu MV, Osiac E, Barbulescu AL, Rheumatology D (2020) JAK/STAT pathway in pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (review). Exp Ther Med 20(4):3498–3503. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8982
Clark AR, Dean JL (2012) The p38 MAPK pathway in rheumatoid arthritis: a sideways look. Open Rheumatol J 6:209–219. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874312901206010209
Malemud CJ (2015) The PI3K/Akt/PTEN/mTOR pathway: a fruitful target for inducing cell death in rheumatoid arthritis? Future Med Chem 7(9):1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.55
Malemud CJ (2007) Growth hormone, VEGF and FGF: involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta 375(1–2):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2006.06.033
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S, Wang JM (1994) Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Stroke 25(9):1794–1798. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.25.9.1794
Palareti G, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Antonucci E, Erba N, Poli D, Testa S, Tosetto A (2016) Comparison between different D-dimer cutoff values to assess the individual risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism: analysis of results obtained in the DULCIS study. Int J Lab Hematol 38(1):42–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijlh.12426
Patra K, Jana S, Sarkar A, Mandal DP, Bhattacharjee S (2019) The inhibition of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis and metastasis by cinnamaldehyde is mediated by decreasing HIF-1α protein synthesis via PI3K/Akt pathway. BioFactors 45(3):401–415. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1499
Cheng CY, Ho TY, Hsiang CY, Tang NY, Hsieh CL, Te KS, Lee YC (2017) Angelica sinensis exerts angiogenic and anti-apoptotic effects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating p38MAPK/HIF-1 α /VEGF-A signaling in rats. Am J Chin Med 45(8):1683–1708. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X17500914
Zhu H, Zhang Y, Zhong Y, Ye Y, Hu X, Gu L (2021) Inflammation-mediated angiogenesis in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci 15:652647. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.652647
Hatakeyama M, Ninomiya I, Kanazawa M (2020) Angiogenesis and neuronal remodeling after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res 15(1):16–19. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.264442
Herpich F, Rincon F (2020) Management of acute ischemic stroke. Crit Care Med 48(11):1654–1663. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000004597
Bansal S, Sangha KS, Khatri P (2013) Drug treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 13(1):57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40256-013-0007-6
Shiojima I, Walsh K (2006) Regulation of cardiac growth and coronary angiogenesis by the Akt/PKB signaling pathway. Genes Dev 20(24):3347–3365. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1492806
Weerackoon N, Gunawardhana KL, Mani A (2021) Wnt signaling cascades and their role in coronary artery health and disease. J Cell Signal 2(1):52–62. https://doi.org/10.33696/Signaling.2.035
Muslin AJ (2008) MAPK signaling in cardiovascular health and disease: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets introduction: intracellular signal transduction pathways. Clin Sci 115(7):203–218. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20070430.MAPK
Kandaswamy E, Zuo L (2018) Recent advances in treatment of coronary artery disease: role of science and technology. Int J Mol Sci 19(2):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020424
Tarkowski E, Issa R, Sjögren M, Wallin A, Blennow K, Tarkowski A, Kumar P (2002) Increased intrathecal levels of the angiogenic factors VEGF and TGF-β in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Neurobiol Aging 23(2):237–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-4580(01)00285-8
Vagnucci AH Jr, Li WW (2003) Alzheimer’s disease and angiogenesis. HYPOTHESIS 361:605–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12521-4
Buée L, Hof PR, Roberts DD, Delacourte A, Morrison JH, Fillit HM (1992) Immunohistochemical identification of thrombospondin in normal human brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 141(4):783–788
Gabbouj S, Ryhänen S, Marttinen M, Wittrahm R, Takalo M, Kemppainen S, Martiskainen H, Tanila H, Haapasalo A (2019) Altered insulin signaling in Alzheimer’s disease brain—special emphasis on PI3K-Akt pathway. Front Neurosci 13:629. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00629
Pohanka M (2018) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease as a target for therapy. Bratisl Lek Listy 119(9):535–543. https://doi.org/10.4149/BLL_2018_097
Rocha AL, Reis FM, Taylor RN (2013) Angiogenesis and endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Int 2013:859619. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/859619
Okada H, Tsuzuki T, Murata H, Kasamatsu A (2016) Regulation of angiogenesis in the human endometrium. Uterine Endometrial Funct. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-55972-6_6
Krikun G (2012) Endometriosis, angiogenesis and tissue factor. Scientifica (Cairo) 2012:306830. https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/306830
Ferrero S, Barra F, Leone Roberti Maggiore U (2018) Current and emerging therapeutics for the management of endometriosis. Drugs 78(10):995–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0928-0
Karampoor S, Zahednasab H, Ramagopalan S, Mehrpour M, Keyvani H (2016) Angiogenic factors are associated with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 301:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.11.005
Girolamo F, Coppola C, Ribatti D, Trojano M, Girolamo F, Coppola C, Ribatti D, Trojano M (2014) Angiogenesis in multiple sclerosis and experime. Acta Neuropathol Commun. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-014-0084-z
Lengfeld J, Cutforth T, Agalliu D (2014) The role of angiogenesis in the pathology of multiple sclerosis. Vasc Cell 6(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13221-014-0023-6
Vidal-Jordana A, Montalban X (2017) Multiple sclerosis: epidemiologic, clinical, and therapeutic aspects. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 27(2):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2016.12.001
Loizzi V, Del VV, Gargano G, De LM, Kardashi A, Naglieri E, Resta L, Cicinelli E, Cormio G (2017) Biological pathways involved in tumor angiogenesis and bevacizumab based anti-angiogenic therapy with special references to ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci 18(9):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091967
Gariano RF, Gardner TW (2005) Retinal angiogenesis in development and disease. Nature 438(7070):960–966. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04482
Cabral T, Mello LGM, Lima LH, Polido J, Regatieri CV, Belfort R Jr, Mahajan VB (2017) Retinal and choroidal angiogenesis : a review of new targets. Int J Retina Vitr. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40942-017-0084-9
Vavvas D, Miller J (2012) Basic mechanisms of pathological retinal and choroidal angiogenesis. Retina Fifth Ed 1:562–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4557-0737-9.00026-6
Gahlaut N, Suarez S, Uddin I, Gordon AY, Evans SM, Jayagopal A (2015) European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics Nanoengineering of therapeutics for retinal vascular disease. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.05.001
Anderson OA, Bainbridge JWB, Shima DT (2010) Delivery of anti-angiogenic molecular therapies for retinal disease. Drug Discov Today 15(7–8):272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2010.02.004
Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J (2004) Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res 23(1):91–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preteyeres.2003.12.001
Acknowledgements
Financial support from the Department of Science and Technology (DST)-INSPIRE [DST/INSPIRE/04/2018/003392] is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JN conceptualized the manuscript and RS wrote the first draft of the manuscript. JN and GP critically reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content. All the authors approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nathan, J., Shameera, R. & Palanivel, G. Studying molecular signaling in major angiogenic diseases. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 2433–2450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04452-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04452-x