What is Reactive Power?
The power that flows in both directions within a circuit, which indicates that it flows in both directions within the circuit or reacts upon itself, is referred to as reactive power. Kilovolt-ampere reactive (kVAR) or megavolt-ampere reactive (MVAR) are the units of measurement for reactive power.
In the cases of an inductor and a capacitor, reactive power indicates that the energy is initially stored, and then later released, in the form of a magnetic field or an electrostatic field, respectively.
Where,
S = Source and
L = Load
Formula to determine Reactive Power:
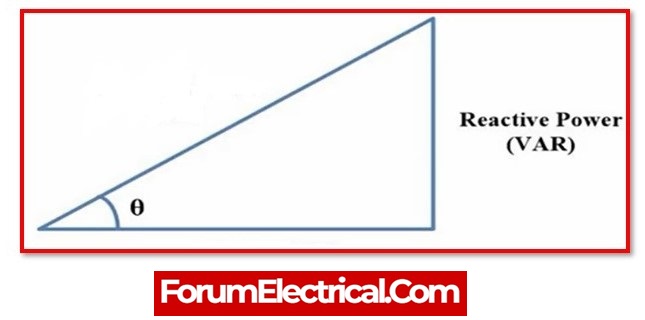
Q = V I SinØ
Where,
V = Voltage,
I = Current and
Ø = Phase Angle
that is either
- Positive (+ve) for inductive loads (or)
- Negative (-ve) for capacitive loads.
The letter “Q” written in capital letters serves as the technical representation for reactive power.
What is the unit of Reactive Power?
The quantity of magnetic or electric field that is created by an inductor or capacitor that is equal to the value produced by one ampere times one volt is referred to as the unit of reactive power.
Volt-Ampere Reactive is the unit of measure for reactive power, abbreviated as VAR, and one VAR is equal to one volt multiplied by one ampere.
i.e., 1 VAR = 1V X 1A
Reactive component:
A reactive component of the current is a current component that is either in quadrature with the voltage on the circuit or is 90 degrees out of phase with the voltage on the circuit and contributes to the reactive power that the circuit possesses.
Advantages of employing Reactive Power:
- Active power is the energy that is delivered in order to run a motor, heat a home, or shine an electric light bulb. Reactive power is the energy that is supplied in order to perform the important task of regulating voltage.
- If the voltage on the system is not high enough, then it will not be possible to supply active power.
- It is required to make use of reactive power in order to create the requisite voltage levels for active power to do productive work.
- Active power cannot reach the user without the input of reactive power as it flows through the transmission and distribution system.
Uses of Reactive Power:
- The primary purpose of reactive power is to control the voltage of the system.
- The usage of reactive power leads to an overall improvement in the effectiveness of the system.