Data Link Layer of OSI Model
FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
The second tier of the OSI Layered Model is the Data Link Layer. This layer is one of the most complex, with several capabilities and liabilities. The data connection layer conceals the specifics of the underlying hardware and represents itself as the channel of communication to the top layer.
The data connection layer communicates between two hosts that are in some ways directly connected. This direct link might be either point-to-point or broadcast. Systems connected to a broadcast network are said to be on the same connection. When dealing with many hosts on a single collision domain, the data connection layer’s task becomes more complicated.
The data connection layer is in charge of transforming data streams to signals bit by bit and transmitting them across the underlying hardware. At the receiver, the data link layer collects data from hardware in the form of electrical signals, then assembles it into a recognised frame format to pass it to a higher layer.
Services Provided By Data Link Layer:
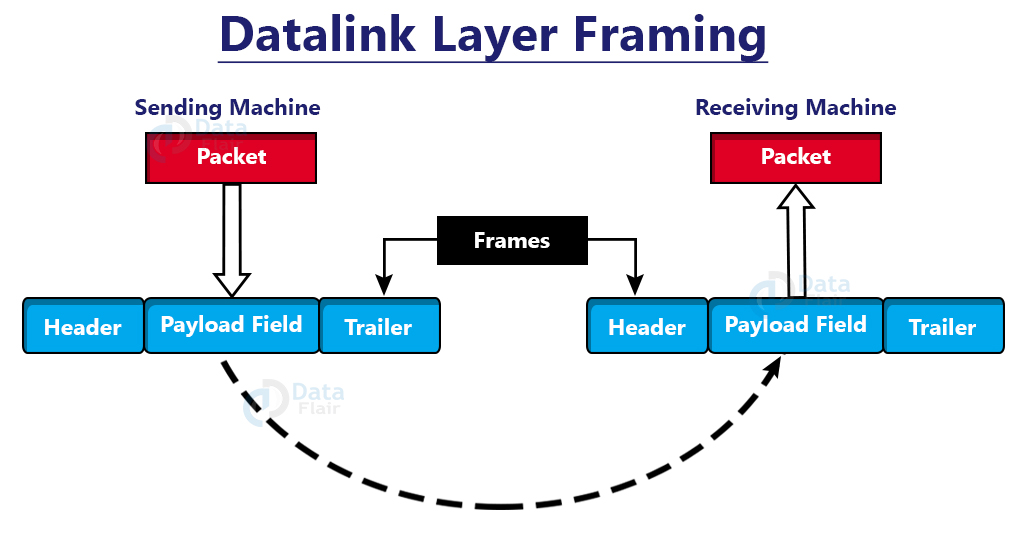
1. Framing:
The data-link layer encapsulates packets from the network layer into frames. Then, on the hardware, it delivers each frame bit by bit. The data connection layer at the receiver’s end collects signals from hardware and assembles them into frames.
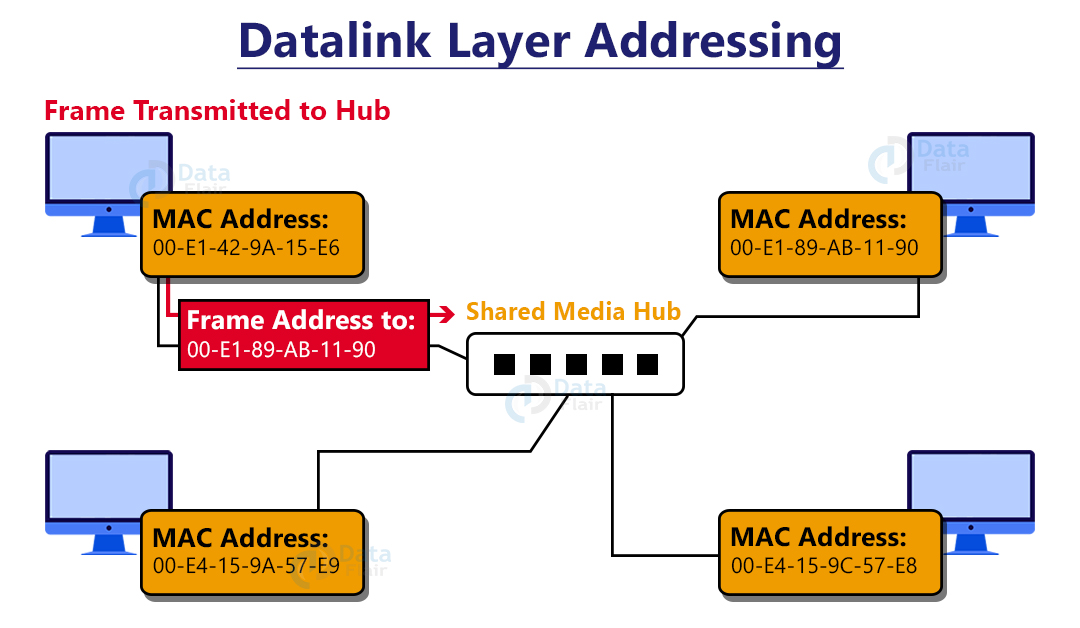
2. Addressing:
Layer-2 hardware addressing is provided by the data-link layer. On the connection, hardware addresses are considered to be unique. It is programmed into devices during the manufacturing process.
3. Synchronization:
When data frames are transmitted via the network, both computers must be synced in order for the transfer to occur.
4. Error Control:
Signals may occasionally meet a difficulty during transition, causing the bits to be flipped. These mistakes are discovered and tried to be recovered in order to retrieve genuine data bits. It also offers the sender with an error reporting tool.
5. Flow Control:
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Stations on the same connection may have varying speeds or capacities. The data-link layer guarantees flow control, allowing two machines to transmit data at the same rate.
6. Multi-Access:
When a host on the shared link tries to send data, there is a significant chance of a collision. The data-link layer offers mechanisms such as CSMA/CD that enable many systems to access a shared medium.
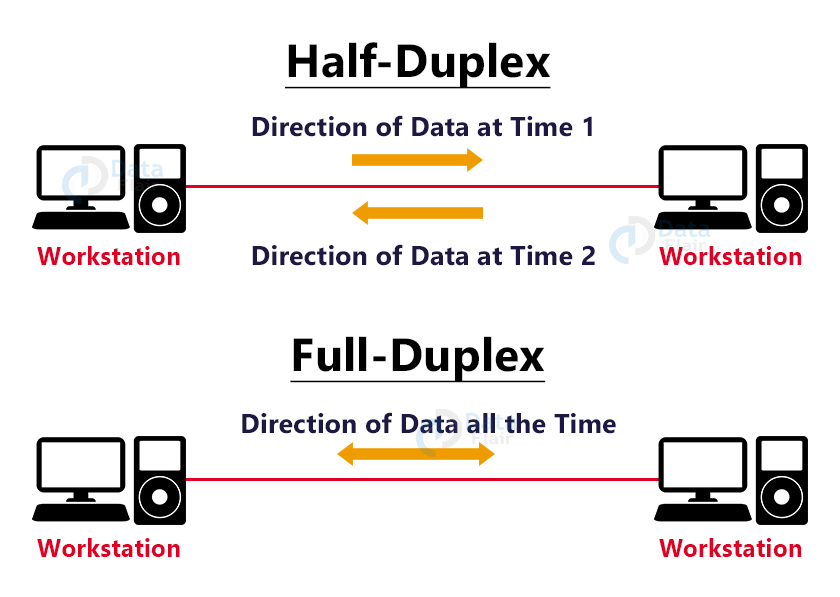
7. Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex:
Both nodes can send data at the same time in Full-Duplex mode. Only one node can send data at the same time in Half-Duplex mode.
8. Reliable Delivery:
The Data Link Layer offers a dependable delivery service, that is, it sends network layer datagrams without error. Transmissions and acknowledgments are used to provide a dependable delivery service. A data connection layer primarily provides a dependable delivery service via links since they have greater error rates and may be rectified locally, rather than causing the data to be retransmitted.
Sub-Layers of Data Link Layer:
1. Logical Link Control:
It is concerned with protocols, flow control, and error control.
2. Media Access Control:
It is concerned with practical media access control.
Data Link Layer Design Issues
The problem with this layer (and much of the upper levels) is how to avoid a fast transmitter from drowning a slow receiver in data. A traffic control method is frequently required to inform the broadcaster of how much buffer space the receiver currently has. Flow regulation and error management are frequently combined.
In this layer, broadcast networks have an additional challenge: how to restrict access to the shared channel. The Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer, a particular sublayer of the data connection layer, deals with this issue.
Summary
In this article, we have covered the data link layer of the OSI model in great detail. We looked at the services provided by it, such as flow and error control, addressing and framing etc. We also looked at the various design issues that this layer is plagued with.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google