WHAT IS CROP ROTATION ?
CROP
ROTATION
WHAT
IS CROP ROTATION
Crop
rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the
same area in sequenced seasons. It is done so that the soil of farms is not
used for only one set of nutrients. It helps in reducing soil erosion and
increases soil fertility and crop yield.
Crop
rotation involves a variety of agricultural techniques, such as tillage, and
the use of fertilizers and chemical pesticide. It also involves land
improvement measures, such as irrigation, drainage and the application of
chemicals for soil improvement.
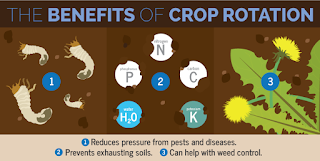
Crop
rotation also prevents plant diseases and pests by exchanging crops that may be
susceptible to a particular diseases or pest with a crop that is not
susceptible. For example, corn is affected by corn root worms, soybeans are not.
The soybeans help suppress the pest so that the corn planted the following year
will not be as adversely affected by it.
There
is no limit to the number of crops in a rotation. Depending on the needs of the
gardener, a large rotation schedule may be implemented and can include the
rotation of animals feed crop like hay, clover or oats. The order in which
crops and fallow succeed each other is called rotation, integrated optimally on
a single farm, make up a crop rotation system.
HOW
CROP ROTATION WORKS
Simply
divide your growing space into a number of distinct areas, identify the crops
you want to grow and then keep plants of the same type together in one area.
Every year the plants grown in each given area are changed, so that each group
(with its own requirements, habits, pests and diseases) can have the advantage
of new ground.
Most
crop rotation schemes tend to run for at least three or four years, as this is
the number of years it takes for most soil-borne pests and diseases to decline
to harmless levels. If your beds are divided into four groups, this means that
members of each plant family won’t occupy the same spot more than once in a
four-year period. It recommends that you
divide crops into four main groups as follows: Legumes (bush
beans, peas, pole beans, broad beans); root vegetables(radish,
carrot, potato, onion, garlic, beet, sweet potato)); leafy
greens (spinach, cabbage, broccoli,
spinach); and fruit-bearing(tomato, sweetcorn, cucumber, pumpkin).
Prepared
by:
MOHAMAD
AMIRUL SHAFIQ BIN FAIZAL ( 2018261668 )
References:
- MAXIMUM YIELD. What does Crop Rotation mean?
- Surabhi Sinha. Crop Rotation- Agriculture
- Kate Bradbury. (12 November 2010). Crop Rotation
- Anne Vezina. Crop Rotation




Comments
Post a Comment